Chapter 10 Human Settlements
Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Answer in short:
Question 1.
Explain the various types of human settlements.
Answer:
(a) Scattered settlements:
- In scattered settlements, houses are few and far from each other.
- They are found in the areas of high relief, dense forests, grasslands, hot deserts and extensive agricultural lands.
(b) Nucleated settlements:
- These settlements are close to water sources like brooks, rivulets, rivers, lakes, reservoirs, etc.
- Fertile plains, transport hubs, mining centres and commercial centres often lead to the development of this type of settlement.
(c) Linear settlements:
- Linear settlements are seen along roads, railways, rivers sea coasts and in foothill regions.
- They are narrow in shape and spread along a straight line.
Question 2.
Difference between nucleated and scattered settlements.
Answer:
| Nucleated Settlements | Scattered Settlements |
| (i) Houses are close together. (ii) These settlements are close to water sources. They are self dependent due to fertile plains, transport hubs, mining centres, defense, health, education and social factors. (iii) People from different castes, religions, races and ideologies live together in these settlements and hence they have a better social life. | (i) Houses are far away from each other. (ii) They depend on centrally located villages for their day to day requirements. Facilities and services in these settlements are not adequate. (iii) These settlements have limited population, so they do not have much social life. |
Question 3.
Explain in natural factors affecting the location of human settlements
Answer:
(a) The natural factors like physiography, land / soils, climate, water supply, river banks, etc. affect the location of human settlements.
(b) Low population & few houses are found in regions of high relief forests, grasslands, hot deserts, etc. whereas high population & nucleated settlements are found in region of fertile plains.
(c) Regions having adequate supply of water has high population & nucleated settlements. Water is essential for occupation of agriculture. Hence early civilizations developed near sources of water like rivers, lakes, reservoirs etc.
(d) In region of extreme climate scattered settlements are found due to difficult living condition whereas in region of favourable climate, nucleated or linear settlements are found.
Question 4.
Explain how human settlements have evolved.
Answer:
- Human settlements have evolved in accordance with the natural conditions.
- Using the resources from his surroundings, man constructed houses and started living in them.
- Rural settlement is the first step towards a stable life in human history.
- Urban settlements have evolved through the expansion and growth of rural settlements.
- There are large scale correlations between rural and urban settlements
- Modernization, science and technology lead to transformation in both types of settlements.
Question 5.
Difference between a hamlet & a village
Answer:
| Hamlet | Village | |
| Size of population is small in a hamlet | (i) | Size of population is comparatively large in a village. |
| Most of people living in a hamlet are engaged a particular occupation which is dependent on locally available natural resource. | (ii) | People in a village are engaged in different occupations like agriculture, fishery, etc. |
| A hamlet is scattered settlement | (iii) | A village is majorly a nucleated settlement. |
2. Identify the types of human settlements from the follwing statements:
Question 1.
Their money and time is saved by living on the farm.
Answer:
Scattered settlements.
Question 2.
There is a lot of social life in this settlement.
Answer:
Nucleated settlements.
Question 3.
Shops are located on both the sides of the road.
Answer:
Linear settlements.
Question 4.
This settlement is found at the foothills of mountains or along the coast.
Answer:
Linear settlements.
Question 5.
Each house is located away from the other.
Answer:
Scattered settlement.
Question 6.
This settlement is good from security point of view.
Answer:
Nucleated settlements.
Question 7.
Having houses away from each other is good for health.
Answer:
Scattered settlements.
Question 8.
The houses are too close to each other.
Answer:
Nucleated settlement.
3. Study the diagram and identify the types of settlements:

Question 1.
Settlement ‘A’ has 5-6 houses and the place does not have other facilities.
Answer:
Scattered settlement.
Question 2.
‘B’ has a high school, a big market and a small theatre.
Answer:
Nucleated settlement.
Question 3.
‘C’ has houses, farmers, many shops and small industries.
Answer:
Linear settlement.
Question 4.
‘D’ has a natural harbour. Many industries have been established here.
Answer:
Linear settlement.
Question 5.
‘C’ is a settlement that has developed along the road side. Give two reasons of its location here.
Answer:
The reasons for settlement ‘C’ developing along the roadside are:
- It has direct & easy access to the main road which helps in easy movement of people & agricultural & industrial goods as houses, farms & small industries are found here.
- It is located at the foothill close to the main river.
ICT Activity :
With the help of the internet, find the image of your village/city. On that basis, write about the type and characteristics of your settlement.
In Text Questions and Answers
Try this
Look at the following picture. Find suitable location for human settlement and show them in picture:
Question 1.
Why were the settlements shown at specific places? Why should they be located there? Why can’t they be located in other places?
Answer:
(i) Settlement A is located at a place which has direct access to main road as well as railway line which will help in easy movement of passenger as well as goods transport.
(ii) Settlement ‘B’ is located on plain land. Its location near a water body will be beneficial for agricultural purpose.
(iii) A large portion of the area shown in the picture is a region of uneven topography which is not favourable for human settlement
Can you tell?
Observe the pictures given in figures (a, b, c, d). Think and answer the following questions:
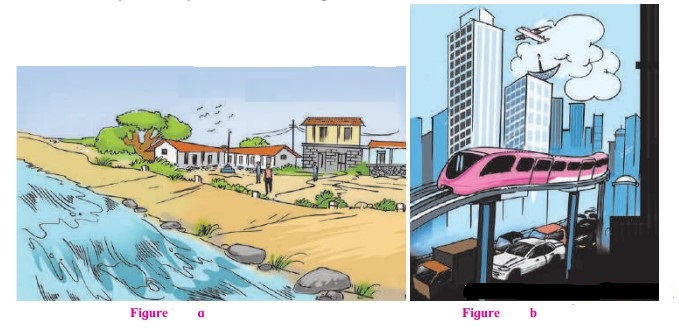

Question 1.
What all can you see in the picture?
Answer:
(a) Rural: settlement small houses made of mud are seen with river flowing and farmland.
(b) City: Monorail, sky scrapers and lot of traffic with vehicles moving.
(c) Tribal hamlet: with sparse1 population.
(d) Town: Vehicles moving, vendors, shops and small houses.
Question 2.
What are the familiar features?
Answer:
All pictures show some type of human settlements.
Question 3.
Which picture shows sparse settlements?
Answer:
Tribal Hamlet shows sparse population.
Question 4.
Which picture shows agriculture?
Answer:
Rural settlement shows agriculture.
Question 5.
Which picture shows dense settlements?
Answer:
City shows dense settlement.
Question 6.
Which picture shows high rise building?
Answer:
City shows high rise building.
Question 7.
From the following, assign a suitable names for each of the pictures: Rural settlement, Tribal hamlet, Town, City.
Answer:
(a) Rural settlements
(b) City
(c) Tribal Hamlet
(d) Town.
Question 8.
Arrange the picture according to the level of development in the settlements?
Answer:
Tribal Hamlets, Rural Settlements, Towns, Cities.
Observe the Fig. and discuss the following questions:

Question 1.
What is the difference between the human settlement at ‘A’ and ‘B’ ?
Answer:
A is Nucleated settlement & ’B’ is a Linear settlement
Question 2.
What is the difference between the settlement at B’ and C ?
Answer:
B is Linear settlement & ‘C’ is a type of tribal hamlet.
Question 3.
Where do you find less than 2 houses?
Answer:
‘C’ is tribal hamlet having less than 2 houses.
Question 4.
In what type of settlement do you live?
Answer:
I stay in ‘A’ type of settlement. (Students may answer as per their settlement type)
Think about it:
Question 1.
Think about the possible processes that take place during the growth and development of settlements. Make a list of such processes.
Answer:
(i) Human settlements rise in places with favourable geographic conditions – such a availability of water, conducive climate, fertile land, etc.
(ii) In such settlements the occupations are majorly based on natural resources. These are called rural settlements.
(iii) With the passage of time, other associated occupations in these settlements grow & people of surrounding areas migrate & settle there, this leading to increase in the population of such settlements.
(iv) The proportion of people engaged in primary occupation declines & the importance of secondary & tertiary occupations increases
leading to transformation of rural settlements into urban settlements.
(v) Over a period of time when the population & the necessary amenities increase on a large scale, the urban areas grow into metropolitan cities.
Give it a try:
Question 1.
Name the metropolitan cities of India.
Answer:
Mumbai, Chennai, Delhi, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Bangalore, Pune, Ahmedabad, etc. are some of the metropolitian cities of India.
Question 2.
Identify the type of settlement where you live.
Answer:
Students are expected to answer this questions on their own.
Question 3.
Observe the photographs given below. Identify the type of settlements shown here and write about them.
Answer:
Fig. 1 is Urban settlement: Houses, schools shops are close to each other. Densely populated.
Fig. 2 is Linear settlement: Houses are built along the Mera Sakharkevda road in three to four rows.
Fig. 3 is a Scattered settlements: Houses are far from each other, sparse population, very little transport.
In Fig. 4 Linear settlements can be seen along the roads whereas scattered settlements also seen
Make friends with maps:
Observe Fig. and answer the following questions:
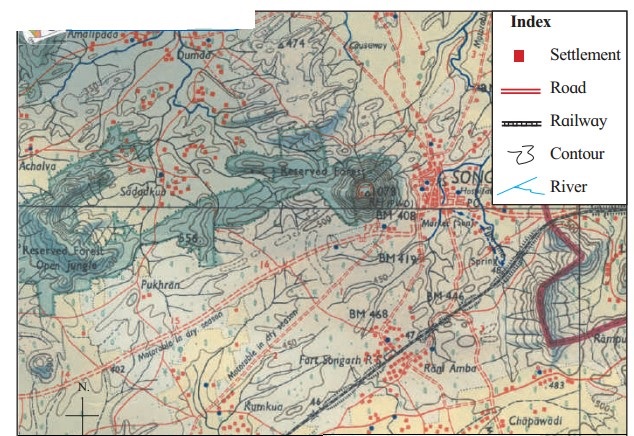
Question 1.
Name some of the settlements shown in the map.
Answer:
Amalipada, Achalva, Sadadkua, Dumda, Pukhram, Rani Amba, Kumkua, Chapawadi, are some settlements shown in the map.
Question 2.
Which of the settlements in the map are in a scattered form?
Answer:
Pukhran, Achalva, Chapawadi and Sadadkua have scattered settlements.
Question 3.
How are the houses in the settlements along the roads arranged?
Answer:
Houses are arranged in a line on both sides of the roads. They are linear settlement.
Question 4.
In which settlements are the houses close together? What could be the reason behind this density?
Answer:
The houses in Sangarh are close together.
Reasons:
- Proximity to river
- Amenities like water pipeline, hospital, post office
- Easy access to transport routes like roads & railways which helps in easy movement of passengers & goods.
Question 5.
Can you now classify the settlements on the basis of these pattern?
Answer:
- Dunda, Sodadkua, Pukhran, etc. have scattered settlements
- Rani Amba is a linear settlement
- Songarh is a nucleated settlement.
Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Human settlements flourished at places with favorable ________ conditions.
Answer:
geographic
Question 2.
In the early settlements, the occupation of the people were dependent on the locally available ________ resources.
Answer:
natural
Question 3.
People along the sea coast are engaged in _______.
Answer:
fishing
Question 4.
Settlements have provided man with _______.
Answer:
stability
Question 5.
In ______ settlements, houses are few and far from each other.
Answer:
scattered²
Question 6.
Increase in the population of rural settlements is the beginning of _________.
Answer:
urbanization
Question 7.
____ settlements are seen along roads, railways, rivers, sea coasts and foot hill regions, etc.
Answer:
Linear
Question 8.
In the deserts of Rajasthan we find _______ settlements.
Answer:
nucleated
Question 9.
_______ is the first step towards a stable life in human history.
Answer:
Rural settlement
Question 10.
Life in urban settlement is more _____.
Answer:
dynamic
Question 11.
_______ settlements have limited population as in small hamlets.
Answer:
Scattered
Complete the following sentence:
Question 1.
Human settlement flourished at places with favourable geographical conditions such as ______.
Answer:
availability of water, a conducive climate, fertile land, etc.
Question 2.
When rural area converts into urban area, the importance of secondary and tertiary occupations increases and _______.
Answer:
the proportion of people engaged in primary occupations decline
Question 3.
If the population and the necessary amenities increase on a large scale ______.
Answer:
the urban areas grow into metropolitan cities.
Question 4.
Patterns of human settlements evolve in _______.
Answer:
accordance with the natural conditions
Question 5.
Increase in population of rural settlements is ______.
Answer:
is the beginning of urbanization
Question 6.
The day to day food requirement of the urban population is _______.
Answer:
fulfilled by rural settlements
Question 7.
In the deserts of Rajasthan we find _______.
Answer:
nucleated settlements near assured sources of water
Question 8.
Linear settlements are seen along _______.
Answer:
roads, railways, rivers, sea coasts and in foothill regions
Question 9.
There are large scale correlations _______.
Answer:
between rural and urban settlements
Question 10.
Urban settlements have evolved through _______.
Answer:
the expansion² and growth of rural settlements
Match the column:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Limited population | (a) Linear settlements |
| (2) Tribal people | (b) Nucleated settlements |
| (3) Have better social life | (c) Scattered settlements |
| (4) On National or State highways | (d) Hamlets |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – d
3 – b
4 – a
Identify the types of human settlements from the following statements:
Question 1.
These settlements are closer to nature, they are free from pollution.
Answer:
Scattered settlements.
Question 2.
Settlements found along the coastal tracts, major rivers and national or state highways.
Answer:
Linear settlements.
Question 3.
These settlements are found in fertile plains, transport hubs and mining centres, commercial centres.
Answer:
Nucleated settlements.
Question 4.
These settlements have limited population and inadequate facilities.
Answer:
Scattered settlements.
Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
Where do human settlements flourish?
Answer:
Human settlements flourish at places with favourable geographic conditions – such as availability of water, a conducive climate, fertile land, etc.
Question 2.
What did forest dwellers or tribal people use for their livelihood?
Answer:
Forest dwellers or tribal people used forest produce for their livelihood.
Question 3.
Where do the farmer & his family live?
Answer:
They live in a house built in or near the fields.
Question 4.
Which settlements are called rural settlements?
Answer:
The settlements where the original occupation of the majority of the people are based on natural resources are called rural settlements.
Question 5.
Wnen do the urban areas grow into metropolitan cities?
Answer:
When the population and the necessary amenities increase on a large scale, the urban areas grow into metropolitan cities.
Question 6.
Where do we find scattered settlements?
Answer:
Scattered settlements are found in the areas of high relief, dense forests, grasslands, hot deserts and extensive agricultural lands.
Question 7.
Where do we find nucleated settlements?
Answer:
Nucleated settlements are generally close to water sources like brooks, rivulets, rivers, lakes reservoirs, etc.
Question 8.
Where do we see Linear settlements?
Answer:
Linear settlements are seen along roads, railways, rivers, sea coasts, in foothill regions, etc.
Question 9.
What makes a city a metropolis?
Answer:
A metropolis is a large city or urban area, which is a significant economic, political and cultural center for a country or region and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce and communications.
Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
Where do human settlements flourish?
Answer:
Human settlements flourish at places with favourable geographic conditions – such as availability of water, a conducive climate, fertile land, etc.
Question 2.
What did forest dwellers or tribal people use for their livelihood?
Answer:
Forest dwellers or tribal people used forest produce for their livelihood.
Question 3.
Where do the farmer & his family live?
Answer:
They live in a house built in or near the fields.
Question 4.
Which settlements are called rural settlements?
Answer:
The settlements where the original occupation of the majority of the people are based on natural resources are called rural settlements.
Question 5.
When do the urban areas grow into metropolitan cities?
Answer:
When the population and the necessary amenities increase on a large scale, the urban areas grow into metropolitan cities.
Question 6.
Where do we find scattered settlements?
Answer:
Scattered settlements are found in the areas of high relief, dense forests, grasslands, hot deserts and extensive agricultural lands.
Question 7.
Where do we find nucleated settlements?
Answer:
Nucleated settlements are generally close to water sources like brooks, rivulets, rivers, lakes reservoirs, etc.
Question 8.
Where do we see Linear settlements?
Answer:
Linear settlements are seen along roads, railways, rivers, sea coasts, in foothill regions, etc.
Question 9.
What makes a city a metropolis?
Answer:
A metropolis is a large city or urban area, which is a significant economic, political and cultural center for a country or region and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce and communications.
Answer in short:
Question 1.
Distinguish between Scattered Settlements & Linear Settlements.
Answer:
| Scattered Settlements | Linear Settlements |
| (i) In scattered settlements houses are far away from each other. (ii) There settlements have limited population as in small hamlets. (iii) These settlements are found in the areas of high relief, dense forest, grasslands, hot deserts and extensive agricultural land | (i) In Linear settlements houses are spread along a straight line. (ii) These settlements have comparatively more population. (iii) These settlements grow along the coastal tracts, major rivers, national or state highways, railways in the foothill regions, etc. |
Question 2.
Describe Linear Settlements.
Answer:
- Linear settlements are seen along roads, railways, rivers, sea coast and in foothill regions, etc.
- Houses in these settlements are along a straight line, in a row.
- As the settlement grows in the course of time, multiple lines emerge.
- Besides houses, some shops can also be seen.
- Such settlements are found along the coastal tracts, major rivers and national of state highways in our country.
Question 3.
What leads to transformation of rural settlement into urban settlement?
Answer:
(i) The settlements where the original occupations of the majority of the people are based on natural resources are called rural settlements. Agriculture, fishery, etc. are some of these occupation
(ii) With the passage of time other associated occupations also develop gradually in these rural settlement.
(iii) As a result people from surrounding areas migrate & settle there leading to an increase in rural population.
(iv) Houses are built & different facilities are developed for the growing population.
(v) Importance of secondary & tertiary occupations increases & the proportion of primary occupations declines.
This process leads to the transformation of rural settlement into urban settlements
Question 4.
Describe man’s future plans in terms of settlements.
Answer:
- Man started using resources from the surroundings.
- Man constructed houses and started living in them.
- They have even built sky-scrapers.
- In future, man is thinking of constructing colonies on other planets and their satellites too.
