Chapter 3 The Union Executive
Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Choose the correct option and rewrite the statement:
Question 1.
In India, the executive power is vested in the ………………. .
(a) President
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Speaker
Answer:
(a) President
Question 2.
The tenure of the President is of ………… years.
(a) three
(b) four
(c) five
Answer:
(c) five
Question 3.
The Council of Ministers is led by the ………………. .
(a) Party Chief
(b) Prime Minister
(c) President
Answer:
(b) Prime Minister
2. Find and write:
Question 1.
The President, the Prime Minister, the Council of Ministers are called the ……………. .
Answer:
Executive
Question 2.
During the Parliamentary session, the period around 12 noon is known as ……………… .
Answer:
Zero hour
3. write the following concepts in your own words:
Question 1.
Impeachment procedure:
Answer:
- The responsibility of protecting the Constitution is shouldered by the President.
- But, if any act of the President violates the Constitution, the Parliament has the authority to remove him.
- This process known as process of Impeachment.
The procedure for impeachment is as follows:
- Anyone House can lay the charge of violation of the Constitution.
- The investigation of the charge is carried out by the other House.
- If the resolution is passed by special (2/3rd) majority of both the Houses, the President can be removed from his post.
Question 2.
No-confidence motion:
Answer:
- In the Parliamentary system of government, the Legislature tries to keep control over the Executive.
- The Executive stays in power till it enjoys the support of the majority in Lok Sabha.
- The members of the Lok Sabha can move a No-confidence motion by simply expressing “We do not have confidence in the government”.
- If the motion is passed with majority support, the Council of Ministers (the Executive) has to resign.
- Thus, this is the most effective way to keep a check on the Council of Ministers.
Question 3.
Jumbo Ministry:
Answer:
- A huge Council of Ministers with more than necessary ministers is referred to as Jumbo Ministry.
- There was a trend to keep large Council of Ministers in our country.
- Later, a constitutional amendment was made to limit the size of the Council of Ministers.
- As per this amendment, the number of ministers in the Council should not be more than 15% of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
4. Answer in brief:
Question 1.
Enumerate the functions of the Council of Ministers.
Answer:
The functions of the Council of Ministers are as follows:
1. The Council of Ministers takes initiative in the process of Law-making by drafting the bills/proposals.
2. It introduces and discusses the bills/ proposals in the House.
3. It introduces bills on various subjects like education, agriculture, industry, health, foreign relations, etc. in the Parliament, conducts discussions on them and tries to get them approved by the Parliament.
4. It also takes the responsibility of implementing the policies approved by the Parliament.
Question 2.
How does the Parliament keep a check on the Executive?
Answer:
The Parliament keeps a check on the Executive in the following ways:
1. The bills/proposals presented by the Council of Ministers are discussed in the Parliament.
2. These discussions and debates help the members to scrutinize the bills/ proposals and point out the shortcomings and help in a creation of healthy laws.
3. During Parliamentary sessions, the proceedings of the House begins with questions asked by the members of the House. The concerned Ministers are expected to give satisfactory answers to these questions.
4. During the Parliamentary sessions, the period around 12 noon is called as ‘Zero House’. During this period, any question of public importance can be raised and discussed.
5. The Parliament can pass a No-confidence motion on the Executive. If the motion is passed with majority support, then it has to resign.
5. Complete the concept picture.
Question 1.
Answer:

Do it:
Find out the text of the oath taken by the President. Understand its meaning with the help of your teachers.
Do you know:
Jumbo Ministry:
- Earlier, there was a trend to keep large Council of Ministers.
- Such huge Councils were known as jumbo Ministry’.
- Later, a constitutional amendment was made to limit the size of the Council of Ministers.
- As per this amendment, the number of ministers in the council should not be more than 15% of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
Can you tell?
What should the members of the Parliament do to participate effectively in debates and discussions?
Understand it :
(The gist of the conversation between Rama and Vidya.)
- The President is the nominal head and the Prime Minister is the executive head.
- The Prime Minister meets the President regularly and informs him about the conduct of administration.
- The President has the right to seek information about new laws and policies framed by the Parliament. from the Prime Minister.
Project:
Question 1.
If you become the Prime Minister what works will you prioritise? Create a priority-wise list and present it in class.
Question 2.
Collect pictures and information of India’s Presidents since independence.
Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct option and rewrite the statement:
Question 1.
The ………………. bears the responsibility of protecting the Constitution and ensuring that the government runs as per the Constitution.
(a) Speaker
(b) President
(c) Vice-President
Answer:
(b) President
Question 2.
The President can be removed if the impeachment resolution is passed by ………………. majority in both the Houses of Parliament.
(a) 1/3rd
(b) 2/3rd
(c) 3/4th
Answer:
(b) 2/3rd
Question 3.
The ………………. is the Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces.
(a) Prime Minister
(b) Vice-President
(c) President
(d) Brigadier
Answer:
(c) President
Question 4.
In case a minister is not a member of the Parliament, he/she has to get elected to the Parliament within ………………. months.
(a) three
(b) six
(c) nine
(d) two
Answer:
(b) six
Question 5.
As per the amendment, the number of minister’s in the council should not be more than ………………. % of the total number of members in Lok Sabha.
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 15
(d) 25
Answer:
(c) 15
Question 6.
The Council of Ministers stays in power till it enjoys the support of majority in ………………. .
(a) Legislative Assembly
(b) Legislative Council
(c) Rajya Sabha
(d) Lok Sabha
Answer:
(d) Lok Sabha
Question 7.
In the absence of the President, ………………. carries out his functions.
(a) Vice-President
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Speaker of Lok Sabha
(d) Chief Election Commissioner
Answer:
(a) Vice-President
Find and write:
Question 1.
The group of Parliamentarians and members of the state legislatures who elect the President ……………… .
Answer:
Electoral college
Question 2.
One who has the right to declare emergency in case of crisis …………… .
Answer:
President
Complete the concept map:
Question 1.
Answer: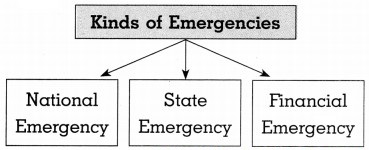
Write short notes on:
Question 1.
Vice-President:
Answer:
- The Vice-President is elected by members of both the Houses.
- The person contesting the election for the post of Vice-President should be a citizen of India and should have completed 35 years of age.
- He is the ex-officio Chairman of Rajya Sabha and exercises control over the functioning of Rajya Sabha.
- In the absence of the President, his functions are carried out by the Vice President.
Question 2.
President:
Answer:
- The President is the Constitutional Head of India.
- He is elected by the directly elected representatives of the Central and State legislatures.
- The person elected to the post of the President has to take an oath while accepting the post.
- According to the oath, the President bears the responsibility of protecting the Constitution and ensuring that the government runs as per the Constitution.
- The President governs in accordance with the advice given by the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers.
- He has Legislative, Executive, Judicial, Defence and Emergency powers.
Explain the following statements with reasons:
Question 1.
The President is the nominal and constitutional Head of India.
Answer:
- The Constitution has vested all executive powers in the President.
- The government carries out its functions in the name of the President.
- However, in reality, the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers run the government.
Hence, the President is the nominal and Constitutional Head of India.
Question 2.
The Council of Ministers has to take the Parliament into confidence while framing policies.
Answer:
- The Council of Ministers has to decide specific policies on subject like education, agriculture, industry, health, foreign affairs, etc.
- The Ministers of respective departments have to lay their policy plans in the House and discuss them thoroughly.
- The policies cannot be implemented without the approval of the Parliament.
- Also, the Council of Ministers can stay in power till it enjoys the support of the Parliament.
- Hence, it has to take the Parliament into confidence while framing policies.
Answer in brief:
Question 1.
How is the President elected?
Answer:
- The President is not directly elected by the people of India.
- The common people do not vote in the election of the President.
- He is elected by the Electoral College.
- The Electoral College includes all members/elected representatives of Parliament and the members of the State Legislatures.
Question 2.
How is the Council of Ministers formed?
Answer:
- The party which attains majority in the Lok Sabha election, nominates its leader as the Prime Minister.
- The Prime Minister is given an oath by the President.
- The Prime Minister then, chooses his trustworthy and efficient colleagues from within the party to form the Council of Ministers.
- He gives priority to his colleagues considering their administrative experience, governance skills, efficiency and technical expertise.
- The President administers oath to all the Council of Ministers. In this way, the Council of Ministers is formed.
Question 3.
State the qualifications necessary for contesting the Presidential election.
Answer:
- The person contesting the Presidential election should be a citizen of India.
- He should be 35 years of age.
- He should also fulfill other conditions mentioned by the Constitution.
Question 4.
Mention the functions of the Prime Minister.
Answer:
The functions of the Prime Minister are as follows:
- To form the Council of Ministers, selecting trustworthy, experienced and efficient people.
- To allocate portfolios and chair all the meetings of the Council of Ministers.
- To lead the Council of Ministers, maintain coordination among various departments, facilitate cooperation among departments and supervise to bring about efficiency and efficacy.
- To raise the image of the country at international level.
- To support the people during disasters.
Question 5.
What should the MPs do to enable them to participate effectively in Lok Sabha discussions?
Answer:
For effective participation in Lok Sabha, the MPs have to practise following things:
- They should come prepared to the Lok Sabha with deep study of the problems of their constituencies and effective solutions to the same.
- They should thoroughly understand the functioning of the Parliament and express people’s problems in a precise manner, without wasting other’s time.
- They should be able to criticise the shortcomings and defects in bills/policies effectively.
- They should be well-versed with the various effective tools, granted by the Constitution, for keeping a check on the Council of Ministers.
- They should strictly keep away from unparliamentary practices like creating chaos, shouting slogans, tearing papers, being physically aggressive or fighting, etc. as such practices are not helpful in any manner.
