Question 1.
First, 6 faced die which is numbered 1 to 6 is thrown, then a 5 faced die which is numbered 1 to 5 is thrown. What is the probability that sum of the numbers on the upper faces of the dice is divisible by 2 or 3?
Solution:
When a 6 faced die and a 5 faced die are thrown, the sample space is
S = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4,4), (4, 5), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5)}
∴ n(S) = 30
Let event A: The sum of the numbers on the upper faces of the dice is divisible by 2.
A = {(1, 1), (1, 3), (1, 5), (2, 2), (2, 4), (3, 1), (3, 3), (3, 5), (4, 2), (4, 4), (5, 1), (5, 3), (5, 5), (6, 2), (6, 4)}
∴ n(A) = 15
Question 2.
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. What is the probability that,
(i) card is either red or black?
(ii) card is either black or a face card?
Solution:

Question 3.
A girl is preparing for National Level Entrance exam and State Level Entrance exam for professional courses. The chances of her cracking National Level exam is 0.42 and that of State Level exam is 0.54. The probability that she clears both the exams is 0.11. Find the probability that
(i) she cracks at least one of the two exams.
(ii) she cracks only one of the two.
(iii) she cracks none.
Solution:
Let event A: The girl cracks the National Level exam.
∴ P(A) = 0.42
Let event B: The girl cracks the State Level exam.
∴ P(B) = 0.54
Also, P(A ∩ B) = 0.11
(i) P(the girl cracks at least one of the two exams)
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
= 0.42 + 0.54 – 0.11
= 0.85
(ii) P(the girl cracks only one of the two exams)
= P(A) – P(B) – 2P(A ∩ B)
= 0.42 + 0.54 – 2(0.11)
= 0.74
(iii) P(the girl cracks none of the exams)
= P(A’ ∩ B’)
= P(A ∪ B)’
= 1 – P(A ∪ B)
= 1 – 0.85
= 0.15
Question 4.
A bag contains 75 tickets numbered from 1 to 75. One ticket is drawn at random. Find the probability that,
(i) number on the ticket is a perfect square or divisible by 4.
(ii) number on the ticket is a prime number or greater than 40.
Solution:

Question 5.
The probability that a student will pass in French is 0.64, will pass in Sociology is 0.45 and will pass in both is 0.40. What is the probability that the student will pass in at least one of the two subjects?
Solution:
Let event A: The student will pass in French.
∴ P(A) = 0.64
Let event B: The student will pass in Sociology.
∴ P(B) = 0.45
Also, P(A ∩ B) = 0.40
∴ Required probability
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
= 0.64 + 0.45 – 0.40
= 0.69
Question 6.
Two fair dice are thrown. Find the probability that the number on the upper face of the first die is 3 or sum of the numbers on their upper faces is 6.
Solution:
When two dice are thrown, the sample space is
S = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}
∴ n(S) = 36
Let event A: The number on the upper face of the first die is 3.
∴ A = {(3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6)}
∴ n(A) = 6
Question 7.
Question 8.
Question 9.
A bag contains 5 red, 4 blue and an unknown number m of green balls. If the probability of getting both the balls green, when two balls are selected at random is 1/7, find m.
Solution:
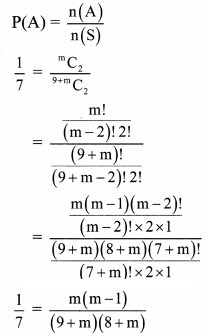
(9 + m)(8 + m) = 7m(m – 1)
72 + 9m + 8m + m2 = 7m2 – 7m
6m2 – 24m – 72 = 0
m2 – 4m – 12 = 0
(m – 6)(m + 2) = 0
m = 6 or m = -2
Since number of balls cannot be negative, m ≠ -2
∴ m = 6
Question 10.
From a group of 4 men, 4 women and 3 children, 4 persons are selected at random. Find the probability that,
(i) no child is selected.
(ii) exactly 2 men are selected.
Solution:
The group consists of 4 men, 4 women and 3 children, i.e., 4 + 4 + 3 = 11 persons.
4 persons are to be selected from this group.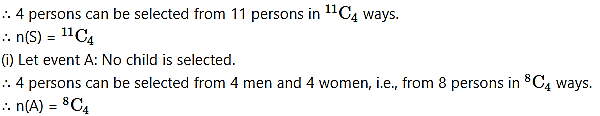
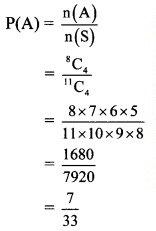
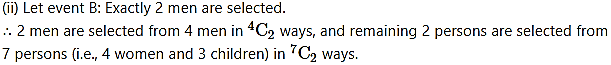
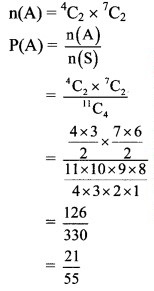
Question 11.
A number is drawn at random from the numbers 1 to 50. Find the probability that it is divisible by 2 or 3 or 10.
Solution:

