1A. Answer in One Sentence:
Question 1.
What is Journal?
Answer:
Journal is a book of account in which all types of day-to-day business transactions are recorded in chronological
order.
Question 2.
What is Narration?
Answer:
Explanation of transaction which is written just below the accounting entry in the particular column is called narration.
Question 3.
What is GST?
Answer:
GST is an abbreviated form of Goods and Service Tax that is levied by the Government on specific goods and services in the place of different taxes levied earlier.
Question 4.
In which year GST was imposed by the Central Government of India?
Answer:
In the year 2017 GST was imposed by the Central Government of India.
Question 5.
What is meant by simple entry?
Answer:
An entry in which only two accounts are affected viz. one account is debited and the other account is credited is called simple entry.
Question 6.
What is the meaning of combined entry?
Answer:
A journal entry that combines more than one debit or more than one credit or both is called a combined/compound entry.
Question 7.
Which account is debited, when rent is paid by Debit card?
Answer:
The rent account is debited when rent is paid by debit card.
Question 8.
Which discount is not recorded in the books of account?
Answer:
Trade discount is not recorded in the books of the account.
Question 9.
In which order monthly transactions are recorded in a Journal?
Answer:
In chronological (date wise) order monthly transactions are recorded in the journal.
Question 10.
Which account is credited, when goods are sold on credit?
Answer:
Sales account is credited, when goods are sold on credit.
2. Give one word/term or phrase for each of the following statements:
Question 1.
A book of prime entry.
Answer:
Journal
Question 2.
The tax imposed by Central Government on Goods and Services.
Answer:
GST
Question 3.
A brief explanation of an entry.
Answer:
Narration
Question 4.
The process of recording transactions in the Journal.
Answer:
Journalising
Question 5.
The French word from which the word Journal is derived.
Answer:
Jour
Question 6.
Concession is given for immediate payment.
Answer:
Cash discount
Question 7.
Entry in which more than one accounts are be debited or credited.
Answer:
Combined Entry
Question 8.
Anything took by the proprietor from the business for his private use.
Answer:
Drawings
Question 9.
Tax payable to the Government on purchase of goods.
Answer:
Input Tax
Question 10.
Page number of the ledger.
Answer:
Ledger Folio
3. Select the most appropriate alternative from the alternatives given below and rewrite the statements.
Question 1.
___________ means explanation of the transactions recorded in the Journal.
(a) Narration
(b) Journalising
(c) Posting
(d) Casting
Answer:
(a) Narration
Question 2.
___________ discount is not recorded in the books of accounts.
(a) Trade
(b) Cash
(c) GST
(d) VAT
Answer:
(a) Trade
Question 3.
Recording of transaction in Journal is called ___________
(a) posting
(b) journalising
(c) narration
(d) prime entry
Answer:
(b) journalising
Question 4.
Every Journal entry require ___________
(a) casting
(b) posting
(c) narration
(d) journalising
Answer:
(c) narration
Question 5.
The ___________ column of the Journal is not recorded at the time of journalising.
(a) date
(b) particulars
(c) ledger folio
(d) amount
Answer:
(c) ledger folio
Question 6.
Goods sold on credit should be debited to ___________
(a) Purchase A/c
(b) Customer A/c
(c) Sales A/c
(d) Cash A/c
Answer:
(b) Customer A/c
Question 7.
Wages paid for installation of Machinery should be debited to ___________
(a) Wages A/c
(b) Machinery A/c
(c) Cash A/c
(d) Installation A/c
Answer:
(b) Machinery A/c
Question 8.
The commission paid to the agent should be debited to ___________
(a) Drawing A/c
(b) Cash A/c
(c) Commission A/c
(d) Agent A/c
Answer:
(c) Commission A/c
Question 9.
Loan taken from Dena Bank should be credited to ___________
(a) Capital A/c
(b) Dena Bank A/c
(c) Cash A/c
(d) Dena Bank Loan A/c
Answer:
(d) Dena Bank Loan A/c
Question 10.
Purchase of animals for cash should be debited to ___________
(a) Livestock A/c
(b) Goods A/c
(c) Cash A/c
(d) Bank A/c
Answer:
(a) Livestock A/c
4. State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons.
Question 1.
Narration is not required for each and every entry.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Correct statement: Narration is required for each and every entry.
Reasons: Narration is a brief explanation of the Journal Entry. It is written in the bracket just below the accounting entry. By reading the narration, the reader understands the meaning and significance of accounting entry and the nature and type of business transactions. Narration should be as short as possible and it should be simple and easy to understand.
Question 2.
A journal voucher is a must for all transactions recorded in the Journal.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Reasons: A voucher is a document that supports a payment made by the businessmen. It is legal evidence that a certain sum of money has been paid to a specific person or party. A Journal voucher is an original or basic voucher on the basis of which business transactions are journalized in the journal. Journal voucher provides legal proof for the business transactions. Therefore a journal voucher is necessary for all transactions recorded in the journal.
Question 3.
Cash discount allowed should be debited to discount A/c.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Reasons: Any allowance or reduction in payment allowed by the seller to the buyer or creditor to the debtor on payment of cash is called cash discount. It is the concession given to encourage prompt payment. The gash discount allowed is an expense or a loss to the receiver. Expenses or Losses are always to be debited. Cash discount allowed is an expense or loss and therefore it is debited to Discount A/c.
Question 4.
Journal is a book of prime entry.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Reasons: Journal is the most important book of accounts. It is a book of daily records. It is the main book of accounts in which transactions are recorded for the first time from source documents. Therefore this book is known as the book of original entry or first entry or prime entry. Business transactions are first entered in the journal and then they are recorded in other accounts book. For these reasons, the journal is called a book of prime entry.
Question 5.
Trade discount is recorded in the books of accounts.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Correct statement: Trade discount is never recorded in the books of accounts.
Reasons: The discount which is allowed or given by the manufacturer to wholesalers and by wholesalers to retailers and retailers to customers on the bulk purchases is called trade discount. By custom or by law trade discount is calculated on the catalog or printed price of the goods. Trade discount is directly deducted from the printed price and net prices of the goods or services are recorded in the books of accounts. A trade discount is given to encourage the buyers to increase their purchases. It is given to traders to enable them to earn a sizeable profit on the printed prices.
Question 6.
Goods lost by theft are debited to the goods account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Correct statement: Goods lost by theft is credited to the goods account.
Reasons: Goods account is a real account because unsold goods are the property of the business. If goods are purchased or acquired, the Goods account is debited and if goods are sold or lost from the business, they are credited. As per the traditional approach, goods lost means go away from the business, and whatever goes out an account of it is credited. As per the modern approach if loss of business increases account of such loss is credited in the hooks of account.
Question 7.
If rent is paid to the landlord, the landlord’s A/c should be debited.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Correct Statement: If rent is paid to the landlord, the Rent account should be debited.
Reasons: Rent paid is an expense and hence it is a nominal account. When rent is paid to the landlord, the rent account is affected and not the landlord’s account. Rent is an expense to a tenant who pays it and it is an income for the landlord. Such payment is not personally due to the landlord as there is no lending and borrowing of money between landlord and rent payer. As per the rule of nominal account, the rent account is debited because it is an expense. As cash goes out cash account is credited.
Question 8.
Book Keeping records monetary and non-monetary transactions.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Correct Statement: Book Keeping records only monetary transactions.
Reasons: According to the money measurement concept, in the books of accounts accountant records only those business transactions which are monetary or financial in nature and capable to be expressed in monetary terms. It means the qualitative and quantitative aspects which cannot be measured in terms of money are not recorded in the books of account personal or non-monetary transactions are not recorded, in the books of accounts e.g. giving lift from car to neighbour, drinking tea along with friends in the restaurant, etc. are not recorded in the books of account as these transactions are not monetary in nature.
Question 9.
Drawings made by the proprietor increase his capital.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Correct statement: Drawings made by the proprietor decreases his capital.
Reasons: Total amount of goods and services withdrawn by the proprietor from the business from time to time for personal use or family use is called drawings. Withdrawals made by a businessman for business purpose is not treated as drawings. Drawings are always adjusted or deducted from capital. Heavy withdrawals made by a businessman for self-use reduces capital in the business. If the businessman controls the drawings more funds are made available for the development of the business. Drawing made by the proprietor reduces his capital investment.
Question 10.
GST paid on the purchase of goods Input tax A/c should be debited.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Reasons: GST is abbreviated from Goods and Service Tax. GST is levied by the government on the purchases of Goods and Services at a specified rate. Since it is imposed on purchases of goods and services, it increases its cost. GST is added to the purchase price. Purchases are always debited and hence GST i.e. Input tax account is also debited along with purchases. In the case of sales of goods and services, the output tax account is credited.
5. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
The first book of original entry is the ___________
Answer:
Journal
Question 2.
The process of recording transaction into journal is called ___________
Answer:
Journalising
Question 3.
An explanation of the transaction recorded in the journal ___________
Answer:
Narration
Question 4.
___________ discount is not recorded in the books of accounts.
Answer:
Trade
Question 5.
___________ is concession allowed for bulk purchase of goods or for immediate payment.
Answer:
Discount
Question 6.
Every Journal Entry requires ___________
Answer:
Narration
Question 7.
___________ discount is always recorded in the books of accounts.
Answer:
Cash
Question 8.
___________ is the document on the basis of which the entry is recorded in the journal.
Answer:
Voucher
Question 9.
There are ___________ parties to a cheque.
Answer:
Three
Question 10.
The ___________ cheque is safer than other cheques as it cannot be encashed on the counter of the bank.
Answer:
Crossed.
6. Specimen and Proforma.
Question 1.
Prepare specimen of Tax Invoice.
Answer: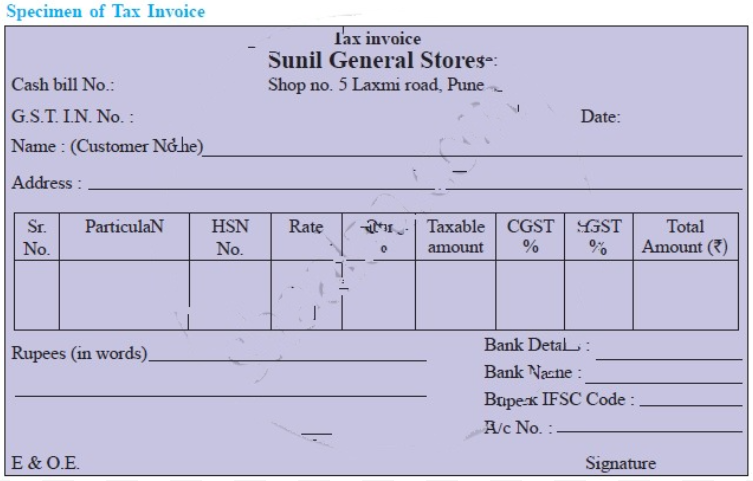
Question 2.
Prepare specimen of Receipt.
Answer: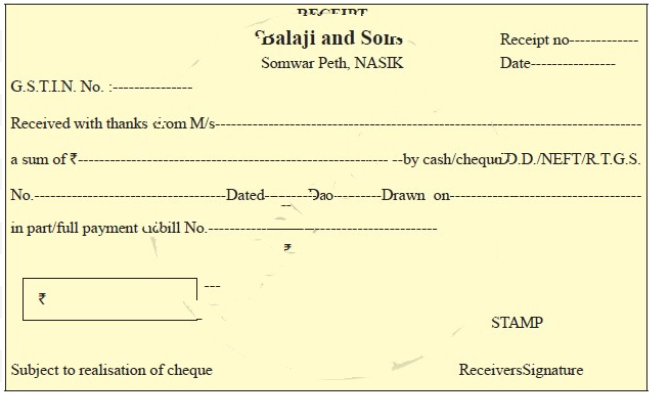
Question 3.
Prepare specimen of the Crossed cheque.
Answer: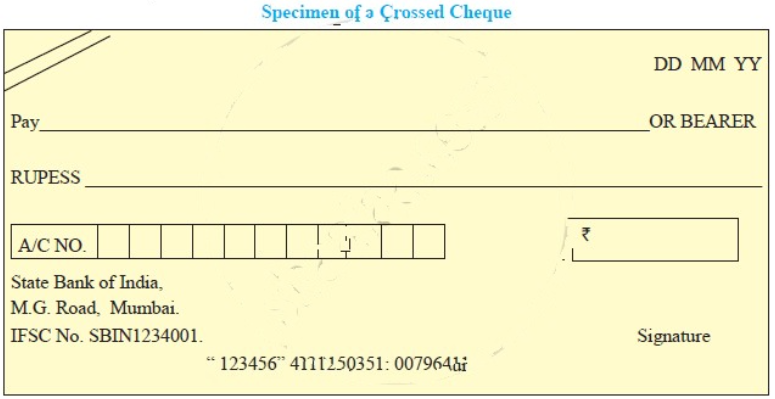
Question 4.
Prepare specimen of Cash voucher.
Answer:
7. Correct the following statements and rewrite the statements.
Question 1.
All business transactions are recorded in the Journal.
Answer:
Only monetary transactions are recorded in the Journal.
Question 2.
A cash discount is not recorded in the books of accounts.
Answer:
A cash discount is recorded in the books of accounts.
Question 3.
Journal is a book of Secondary entry.
Answer:
Journal is a book of Prime entry.
Question 4.
GST is imposed by the Government of India from 1st July 2018.
Answer:
GST is imposed by the Government of India from 1st July 2017.
Question 5.
The machinery purchased by the Proprietor decreases his capital.
Answer:
Machinery purchased by the proprietor increases his Capital.
8. Do you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Question 1.
Narration is required for every entry.
Answer:
Agree
Question 2.
GST stands for Goods and Sales Tax.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 3.
Trade discount is not recorded in the books of accounts.
Answer:
Agree
Question 4.
Wages paid for the installation of Machinery is debited to Wages Account.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 5.
The process of entering or recording the transactions in a Journal is called Journalising.
Answer:
Agree
9. Calculate the following:
Question 1.
Purchased Motor Car from Tata & Company worth ₹ 2,00,000 at 18% GST. Find out GST amount.
Solution:
Cost of the Motor Car = ₹ 2,00,000
GST @ 18% = 2,00,000 × = ₹ 36,000
Net value of the Motor Car = ₹ 2,00,000 + ₹ 36,000 = ₹ 2,36,000
Question 2.
Paid Transport charges ₹ 10,000 @ 5% GST. Calculate CGST & SGST.
Solution:
Transport charges = ₹ 10,000 @ 5% GST.
CGST = Transport charges × 2.5%.
= 10,000 ×
= 10,000 ×
= ₹ 250
SGST = Transport charges × 2.5%.
= 10,000 ×
= 10,000 ×
= ₹ 250
Net value = 10,000 + 250 + 250 = ₹ 10,500.
Question 3.
Bought goods from Ranjan ₹ 10,000 @ 5% GST and 10% cash discount. Calculate cash discount.
Solution:
Cost of the goods bought = ₹ 10,000 @ 5% GST and 10% cash discount.
GST on Goods Purchased = Cost of goods × 5%.
= 10,000 ×
= ₹ 500.
Net value of Goods Purchased = 10,000 + 500 = ₹ 10,500
Cash discount = Net value × 10%.
= 10,500 ×
= ₹ 1,050.
Question 4.
Received cheque of ₹ 90,000 from Kiran in full settlement of his account ₹ 1,00,000/-. Calculate discount rate.
Solution:
Discount allowed to Kiran = Amount due – Amount received
= 1,00,000 – 90,000
= ₹ 10,000.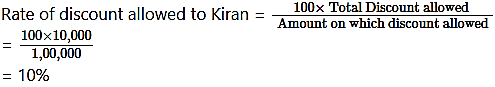
Question 5.
Sold goods of ₹ 1,00,000 at 10% Trade Discount and 10% cash discount to Ram and received 50% amount by cheque. Calculate the amount of cheque received.
Solution:
Trade Discount = Catalogue price × Rate of trade discount
= 1,00,000 ×
= ₹ 10,000
Net amount receivable = Catalogue price – Trade Discount
= 1,00,000 – 10,000
= ₹ 90,000
50% of net amount received.
∴ Amount receivable = 50% of 90,000
= × 90,000
= ₹ 45,000
Cash discount allowed = 10% on ₹ 45,000
= × 45,000
= ₹ 4,500
Amount of cheque received = 50% of total amount – Cash discount
= 45,000 – 4,500
= ₹ 40, 500
Amount received by cheque = ₹ 40,500.
10. Complete the following table.
Question 1.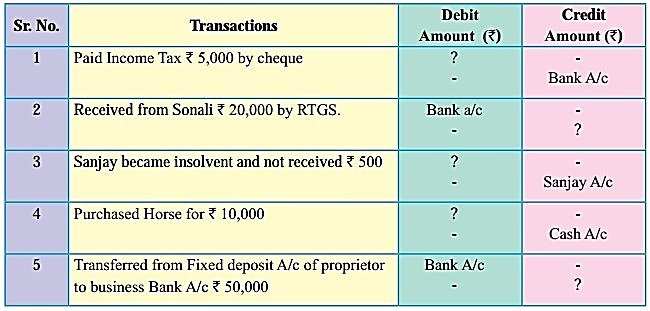
Answer:
1. Drawings A/c
2. Sonali’s A/c
3. Bad debts A/c
4. Livestock A/c
5. Capital A/c
Practical Problems
Question 1.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Anand General Merchants.
2019 April
1 Mr. Anand started the business with cash of ₹ 60,000.
5 Purchased goods for cash ₹ 30,000.
7 Sold goods of ₹ 10,000 to Suresh.
10 Purchased Furniture from Mr. Govind on credit ₹ 30,000.
15 Paid for Rent ₹ 3000 and paid by debit card.
21 Purchased goods from Urmila on credit ₹ 70,000.
27 Paid for Transport ₹ 1,000 to United Transport.
30 Paid to Urmila ₹ 20,000 on behalf of Sharmila.
Solution:
In the Journal of Anand General Merchants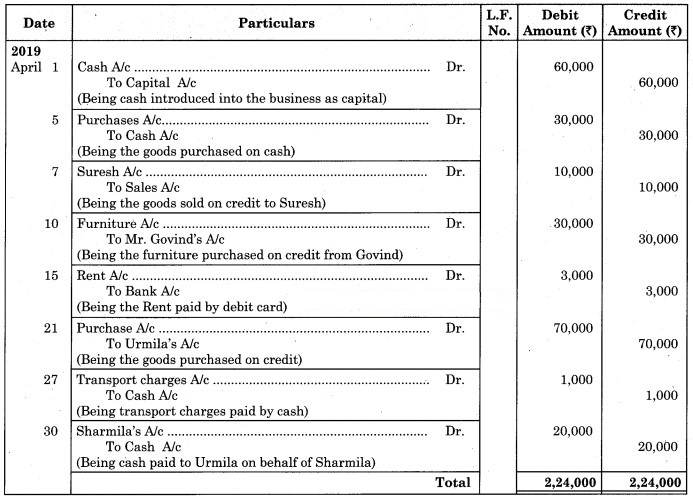
Question 2.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Gajanan.
2019 May
3 Purchased goods for ₹ 90,000 and amounts paid by Bank directly.
7 Sold goods to Satish on credit ₹ 30,000.
9 Paid for Postage ₹ 10,000.
12 Paid for Wages ₹ 15,000.
15 Received cheque of ₹ 30,000 from Satish.
21 Received Dividend ₹ 5000.
25 Purchased Laptop of ₹ 40,000 and paid by cheque.
28 Deposited cash ₹ 10,000 into State Bank of India.
31 Purchased goods for ₹ 40,000 and paid by RTGS.
Solution:
Journal of Gajanan
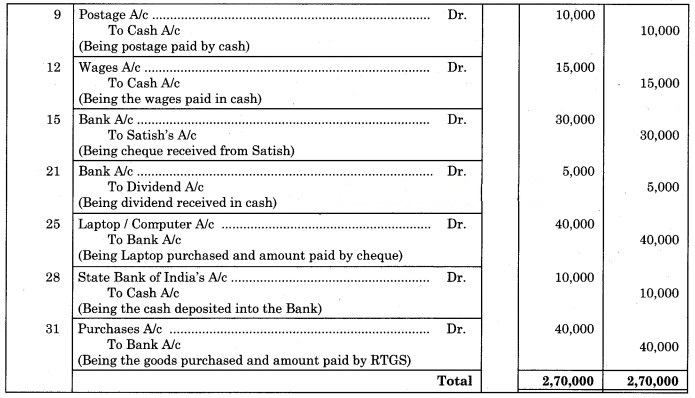
Question 3.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Ashok General Stores.
2019 May
1 Received ₹ 5,000 from Ram on behalf of Bharat.
4 Purchased Goods for cash ₹ 55,000.
8 Paid for Salary ₹ 8,000.
12 Purchased goods from Ganesh ₹ 30,000 on credit.
17 Sold goods to Mrs. Neha ₹ 60,000 on credit.
20 Purchased Machinery of ₹ 80,000 @ 12% GST and amount paid by cheque.
25 Paid to SG & Sons by cheque ₹ 30,000.
28 Received Commission ₹ 10,000 from Ganesh.
30 Paid Rent ₹ 5000.
31 Purchased Shares of Atul Company Ltd. for ₹ 10,000 through Demat account.
Solution:
Journal of Ashok General Stores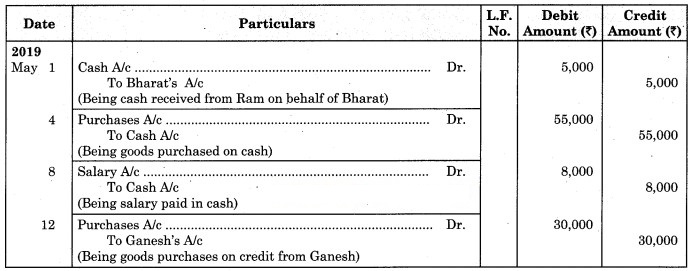
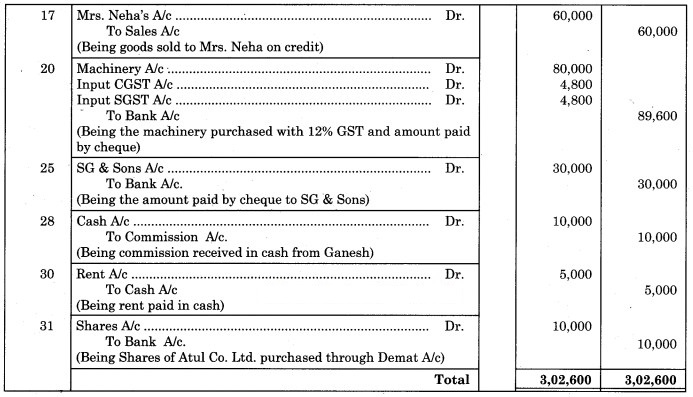
Working Note:
Dated 20th May 2019:
Calculation of CGST and SGST on Machinery
Catalogue price of ₹ 80,000 @ 12%.
CGST i.e. Central Goods and Services Tax = 12% × = 6%.
CGST = Price of Machinery × 6%.
= 80,000 ×
= ₹ 4,800.
SGST i.e. State Goods and Service Tax = 12% × = 6%.
SGST = 80,000 × = ₹ 4,800.
Question 4.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Sanjay General Stores.
2019 June
1 Started business with cash ₹ 50,000, Bank ₹ 1,00,000, Goods worth ₹ 50,000.
5 Purchased goods from Mohan on credit ₹ 80,000 at 10% Trade Discount.
9 Sold goods to Urmila ₹ 30,000 at 5% Trade Discount.
12 Paid into Dena Bank ₹ 40,000.
15 Goods worth ₹ 5000 were distributed as a free samples.
22 Paid for Commission ₹ 5,000 to Anand.
24 Received ₹ 28,000 from Urmila in full settlement of her account by Debit Card.
29 Paid for Advertisement ₹ 9,000.
30 Purchased Laptop for ₹ 20,000 @ 28% GST and amount paid by NEFT.
Solution:
Journal of Sanjay General Stores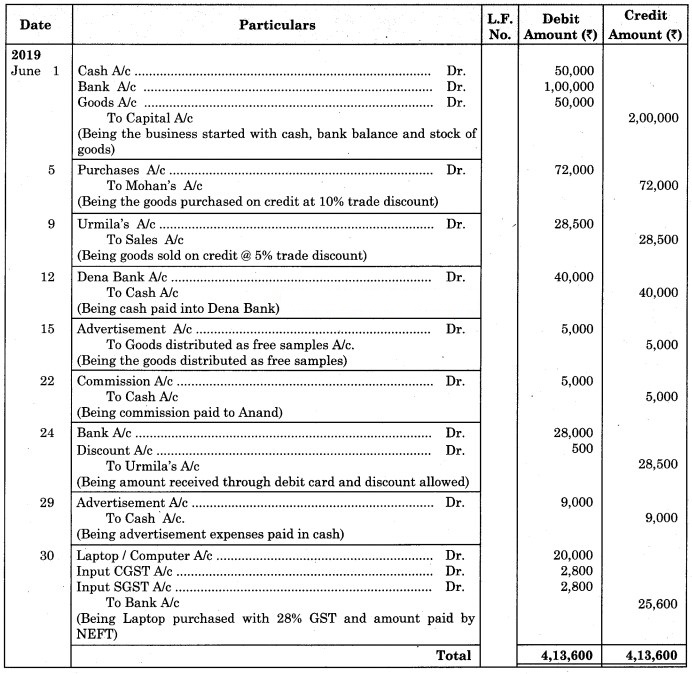
Working Note:
5th June 2019:
Calculation of Trade discount
Purchased goods for ₹ 80,000 @ 10% Trade discount
Trade discount = 80,000 × = ₹ 8,000
Net Purchase Price = 80,000 – 8,000 = ₹ 72,000
24th June 2019:
Discount allowed to Urmila = Amount due – Amount received
= 28,500 – 28,000
= ₹ 500
30th June 2019:
Calculation of CGST and SGST
Price of Laptop = ₹ 20,000 @ 28% GST.
CGST = (Price of Laptop) × Rate of CGST
= 20,000 ×
= ₹ 2,800
SGST = (Price of Laptop) × Rate of SGST
= 20,000 ×
= ₹ 2,800
Question 5.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Kunal Stores.
2018 August
1 Purchased goods of ₹ 90,000 at 10% Trade Discount and 10% Cash Discount from Rakesh and 1/3rd amount paid by cheque.
5 Opened current account in State Bank of India by depositing ₹ 60,000.
8 Cash purchases ₹ 85,000.
10 Goods sold on credit to Tushar ₹ 20,000 @ 10% Trade Discount.
12 Paid Salary ₹ 4,000.
16 Tushar returned goods of ₹ 250.
17 Goods taken by Kunal for his private use ₹ 2,000.
20 Purchased Laptop of ₹ 40,000 from Joshi Electronics @ 18% GST and paid by cheque.
22 Rent paid by cheque ₹ 15,000.
25 Purchased Motor car worth ₹ 2,00,000 for cash @ 18% GST and paid by Bank.
26 Goods distributed as free sample ₹ 4,000.
28 Purchased goods from Amit of ₹ 60,000 on credit.
30 Paid by ECS cash to Amit ₹ 58,500, who allowed us a discount of ₹ 1,500.
30 Sold goods ₹ 5,000 at a loss of ₹ 1,000
31 Sold goods for ₹ 20,000.
Solution:
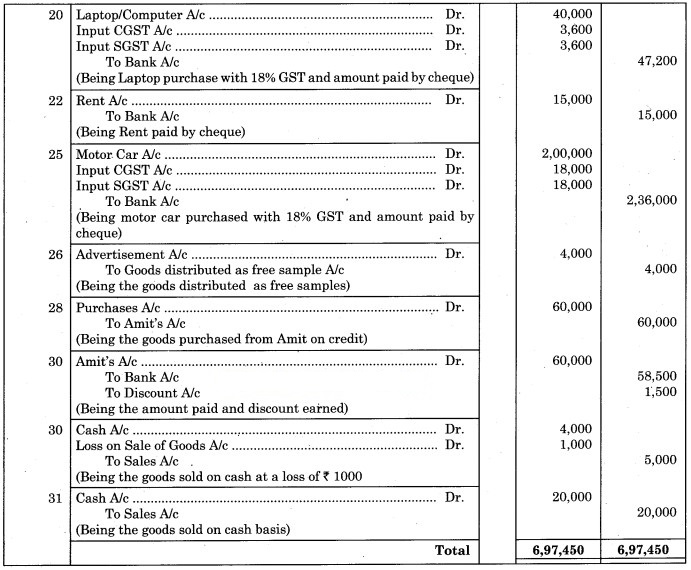
Journal of Kunal Stores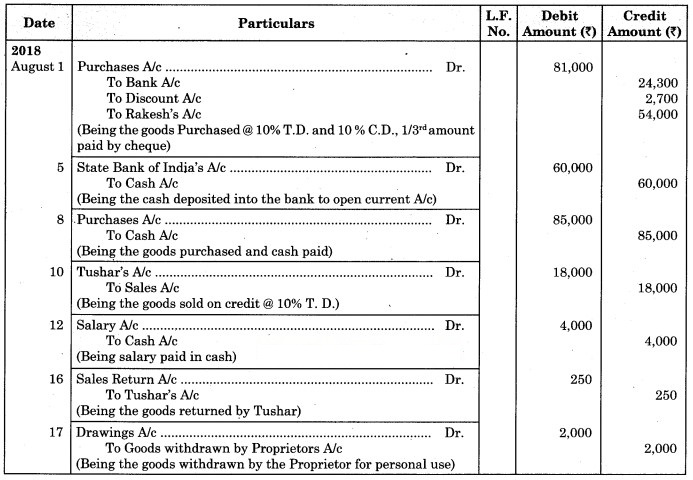
Working Notes:
1. 2018 Aug. 1st:
Trade discount = 10% on Purchase catalogue price
= × 90,000
= ₹ 9,000
Net Purchase price = 90,000 – 90,00 = ₹ 81,000
Amount paid = × 81,000 = ₹ 27,000
Cash discount = 10% on 27,000
= × 27,000
= ₹ 2700
Amount paid by cheque = 27,000 – 2700 = ₹ 24,300
2. Aug. 10th:
Net price of Goods sold to Tushar = 20,000 – 10% Trade discount
= 20,000 – × 20,000
= 20,000 – 2,000
= ₹ 18,000
3. 20th Aug. 2018:
Calculation of GST
CGST = 9% on ₹ 40,000
= × 40,000
= ₹ 3,600
SGST = 9% on ₹ 40,000
= × 40,000
= ₹ 3,600
4. 25th Aug. 2018:
Calculation of GST
CGST = 9% on ₹ 2,00,000
= × 2,00,000
= ₹ 18,000
SGST = 9% on ₹ 2,00,000
= × 2,00,000
= ₹ 18,000
Question 6.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Nina General Stores.
2018 Sept
1 Sold goods of ₹ 50,000 at 10% Trade Discount and 10% Cash Discount to Raj and received 50% by cheque and 20% by cash.
3 Bought goods worth ₹ 60,000 from Prashant at 7.5% Trade Discount and half amount paid by cash.
5 Returned goods worth ₹ 550 to Prashant.
7 Sold goods worth ₹ 90,000 to Ranvir on credit at 10% Trade Discount.
12 Received Commission ₹ 4,500.
15 Received cheque of ₹ 80,000 from Ranvir in full settlement of his account.
18 Purchased Computer worth ₹ 80,000 from Reliance Company by cheque at 28% GST.
22 Wages paid ₹ 13,000.
23 Paid for Life Insurance premium ₹ 17,000.
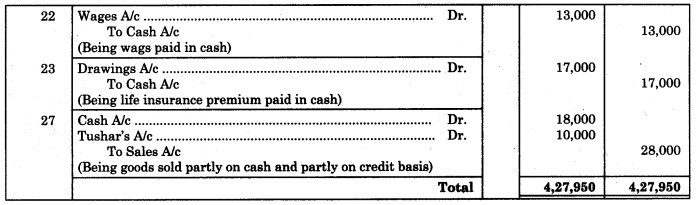
27 Sold goods worth ₹ 28,000 to Tushar who paid us ₹ 18,000 immediately
Solution:
Journal of Nina General Stores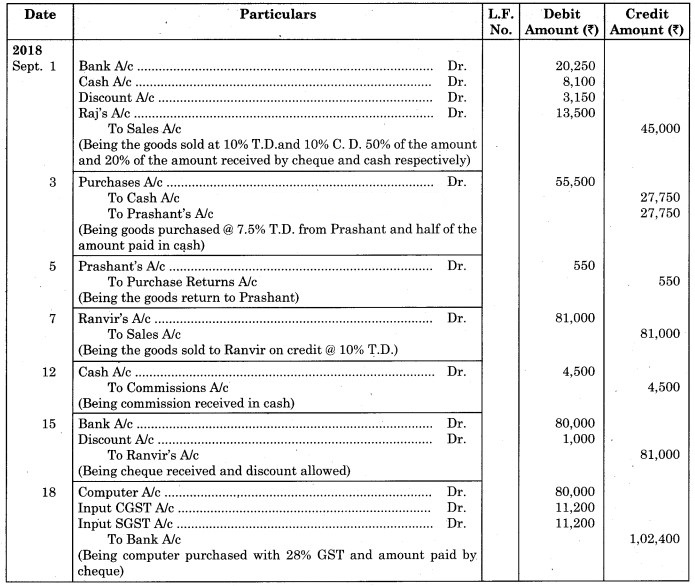
Working Notes:
1. 1st Sept. 2018:
Selling (invoice) price = ₹ 50,000
Trade Discount = 10% on ₹ 50,000
= × 50,000
= ₹ 5,000
Net selling price = 50,000 – 5,000 = ₹ 45,000
50% of the Net selling price received by cheque
Amount of cheque received = 50% of Net selling price – Cash discount
= × 45,000 – 10% on ₹ 22,500
= 22,500 – 2,250
= ₹ 20,250
20% of Net selling price received by cash.
Net amount of cash received = 20% of Net selling price – Cash discount
= × 45,000 – Cash discount
= 9,000 – × 9000
= 9,000 – 900
= ₹ 8,100
30% of Net Selling price is not received
∴ Amount not received = × 45,000 = ₹ 13,500
Total of cash discount = 2,250 + 900 = ₹ 3,150
2. 3rd Sept. 18:
Trade discount = 7.5% on 60,000
= × 60,000
= ₹ 4,500
Net Purchase price = 60,000 – 4,500 = ₹ 55,500
3. 18th Sept. 18:
Calculation of GST
CGST = (Purchase Price of Computer) × 14%
= 80,000 ×
= ₹ 11,200
SGST = 80,000 × = ₹ 11,200
Net Purchase price of Computer = 80,000 + 11,200 + 11,200 = ₹ 1,02,400
Question 7.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Varun
2018 Oct.
1 Purchased Machinery of ₹ 95,000 and paid ₹ 5,000 for freight.
3 Purchased goods for ₹ 1,50,000 and amount paid by Bank.
6 Purchased Laptop from Nagesh & Co. worth ₹ 1,80,000 @ 18% GST.
10 Paid into Bank of Baroda ₹ 70,000.
12 Paid for Rent ₹ 4,000 and Commission ₹ 3,000.
15 Bought goods from Tushar Company Ltd. ₹ 1,20,000 at 12% GST and paid 1/2 amount by RTGS.
16 Cash purchases ₹ 50,000 amount paid by cheque.
20 Invoiced goods to Satish ₹ 80,000 at 12% GST and the amount received by cheque.
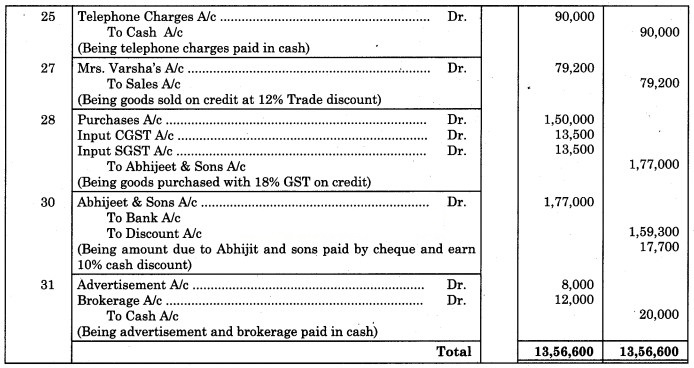
25 Paid for Telephone charges ₹ 90,000
27 Mrs. Varsha bought goods from us ₹ 90,000 at a 12% Trade Discount.
28 Purchased goods from Abhijeet & Sons ₹ 1,50,000 at 18% GST.
30 Paid to Abhijeet & Sons and received 10% Cash Discount by cheque.
31 Paid for Advertisement ₹ 8,000 and Brokerage ₹ 12,000.
Solution:
Journal of Varun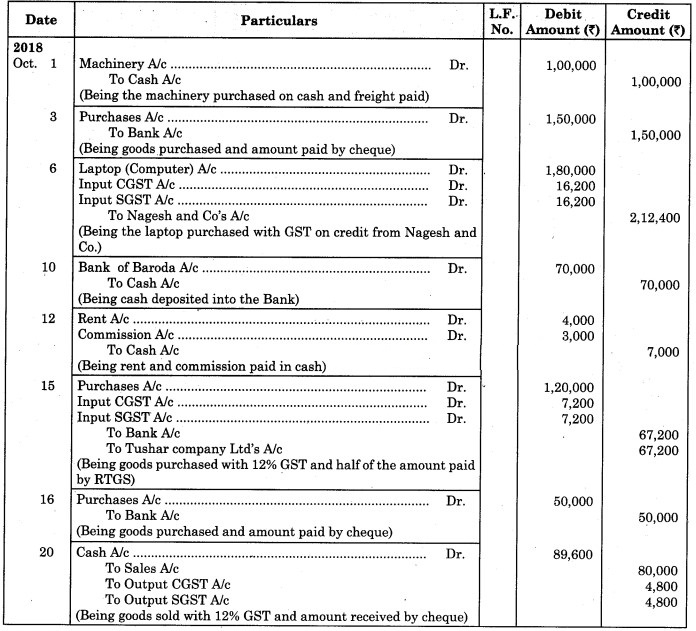
Question 8.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Dhoni Auto Car Centre
2018 Nov
1 Sold 1,000 shares for ₹ 100 each and paid brokerage @ 1% and the amount credited to our account.
4 Purchased goods from Ashish & Co. of ₹ 2,00,000.
6 Sold goods to Virat & Co. ₹ 1,50,000.
8 Paid for Advertisement ₹ 30,000 to Times of India.
10 Paid for Printing and Stationery ₹ 7,000.
12 Purchased goods from Prakash & Co. ₹ 1,50,000 @ 18% GST.
15 Paid for Transport charges ₹ 10,000 @12% GST.
20 Purchased goods from Vikram & Sons ₹ 1,20,000 @ 18% GST and paid half the amount immediately.
25 Paid to Prakash & Co. less 10% discount.
30 Invoiced Goods to Sanjay ₹ 60,000.
31 Sanjay returned goods of ₹ 10,000.
31 Sanjay became insolvent and recovered only 50 paise in a rupee as a final settlement from him.
Solution:
Journal of Dhoni Auto Car Centre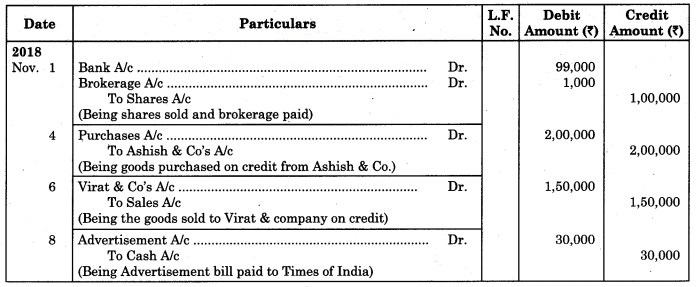
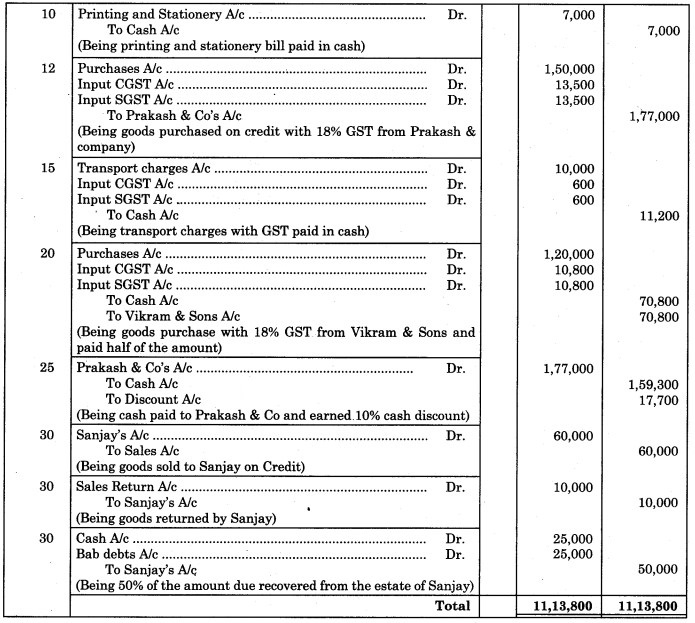
Working Notes:
1. 2018, Nov. 1:
Amount credited to Bank A/c = Sales proceed – Brokerage @ 1%
= 1,000 × 100 – × 1,000 × 100
= 1,00,00 – 1,000
= ₹ 99,000
2. Nov. 12:
Net Purchase price = Purchase price + 9% CGST + 9% SGST
= 1,50,000 + × 1,50,000 + × 1,50,000
= 1,50,000 + 13,500 + 13,500
= ₹ 1,77,000
3. Nov. 20:
Net Purchase price = Purchase price + 9% CGST + 9% SGST
= 1,20,000 + × 1,20,000 + × 1,20,000
= 1,20,000 + 10,800 + 10,800
= ₹ 1,41,600
Amount paid = of 1,41,600 = ₹ 70,800 and credit purchased = ₹ 70,800.
4. Nov. 25:
Cash discount = Amount due to Prakash & Co × 10%
= 1,77,000 ×
= ₹ 17,700
5. Bad debts = Amount due from Sanjay – Amount recovered
= 50,000 – 50% of 50,000
= 50,000 – 25,000
= ₹ 25,000
Question 9.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Hero Enterprises.
Balance on 1st April 2019
Cash at Bank ₹ 80,000, Sundry Debtors Ram ₹ 20,000, Rahim ₹ 30,000, Stock ₹ 55,000, Building ₹ 1,50,000.
Credit Balances on 1st April 2019
Sundry Creditors Swapna ₹ 20,000, Rohit ₹ 30,000, Bank Loan ₹ 50,000.
2019 April
1 Purchased goods worth ₹ 1,50,000 from Prashant & Co., less 10% Trade Discount.
4 Sold goods to Mr. Amit Sharma ₹ 70,000 at 10% Trade Discount on credit.
9 Purchased goods for cash ₹ 2,00,000 @ 28% GST amount paid by NEFT.
12 Sold Goods to Aditya Ray of ₹ 90,000 @ 28% GST.
15 Paid for Rent ₹ 5000 and Salary ₹ 18,000.
17 Paid for Proprietor’s house Rent ₹ 12,000.
20 Sold half of the goods purchased on 9th April at 20% Profit and 28% GST.
25 Paid for Wages ₹ 1,500.
25 Purchased Furniture ₹ 1,80,000 @ 12% GST and amount paid by RTGS.
28 Sold an old Furniture of ₹ 20,000 for ₹ 12,000.
30 Sold shares of ₹ 10,000 for ₹ 15,000 and the amount received by cheque.
Solution:
Journal of Hero Enterprises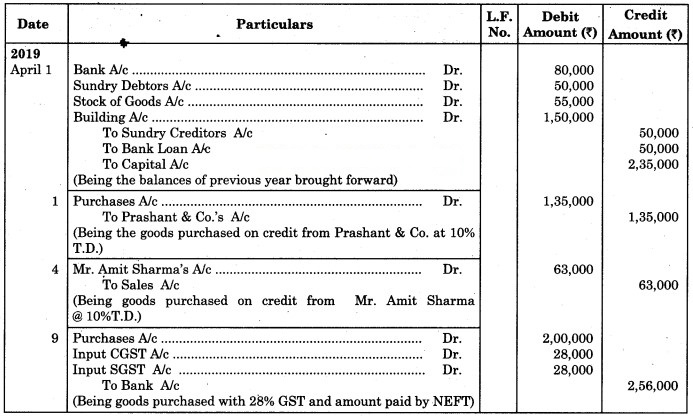
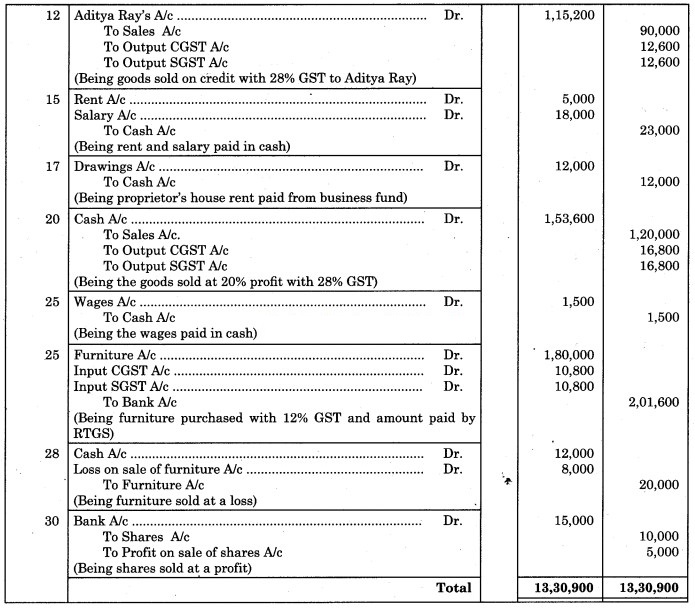
Working Notes:
1. 2019 April, 20:
Cost of Goods sold = of purchases on 9th April, 2019
= × 2,00,000
= ₹ 1,00,000
Selling price of Goods sold = × ₹ 1,00,000 = ₹ 1,20,000
2. April, 28:
Loss on sale of furniture = Cost of furniture – Selling price
= 20,000 -12,000
= ₹ 8,000
3. April, 30:
Profit on sale of shares = Selling price – Cost of shares
= 15,000 – 10,000
= ₹ 5,000
Question 10.
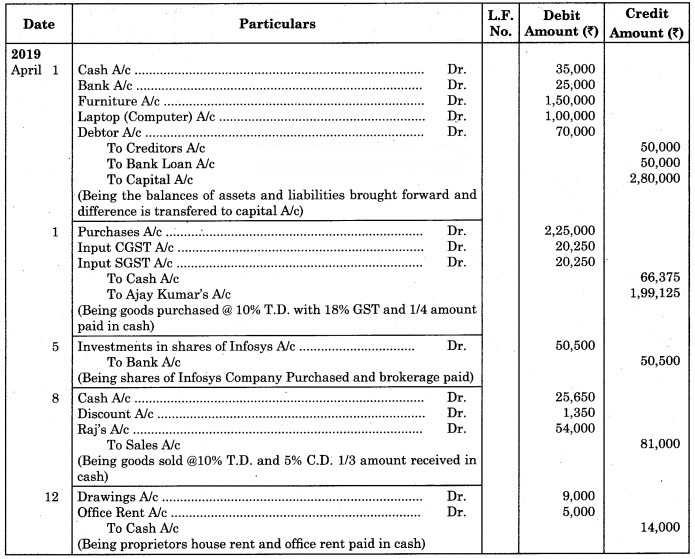
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Harbhajan & Co. for the month of 1st April 2019.
Balance on 1st April 2019
Cash in hand ₹ 35,000, Cash at Bank ₹ 25,000, Furniture ₹ 1,50,000, Laptop ₹ 1,00,000
Debtors: Sangita ₹ 40,000, Viru ₹ 30,000
Creditors: Ganesh ₹ 10,000, Garima ₹ 40,000, Bank loan ₹ 50,000.
2019 April
1 Purchased goods from Ajay Kumar worth ₹ 2,50,000 at 10% Trade discount @ 18% GST and paid 1/4 amount in Cash.
5 Purchased shares of Infosys Company ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 500 paid as a brokerage for Demat A/c.
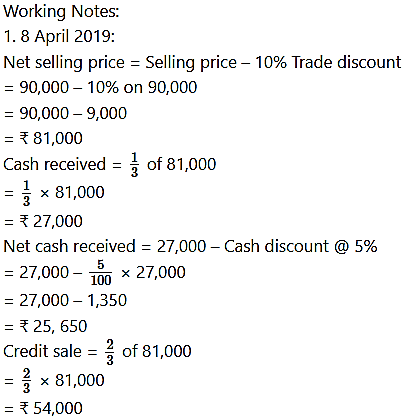
8 Sold goods to Raj worth ₹ 90,000 at 10% Trade discount and 1/3 amount received by cash and 5% cash discount is allowed.
12 Paid house rent of proprietor ₹ 9,000 and office rent ₹ 5,000.
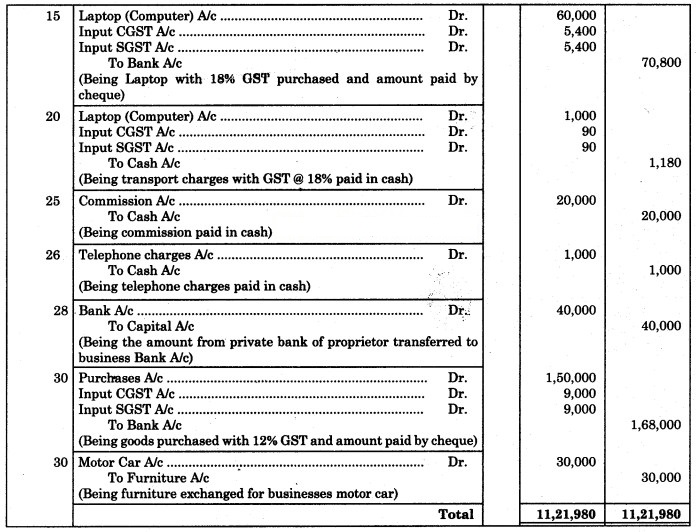
15 Purchased Laptop of ₹ 60,000 @ 18% GST and paid amount by cheque.
20 Paid transport charges on the above Laptop ₹ 1,000 @ 18% GST.
25 Paid Commission ₹ 20,000 to Ram.
26 Paid Telephone Charges ₹ 1,000.
28 Transferred from private Bank A/c of proprietor to business Bank A/c ₹ 40,000.
30 Bought goods for ₹ 1,50,000 @ 12% as GST by cheque.
30 Exchanged our Furniture of ₹ 30,000 against a Motor car of the same value for business.
Solution:
Journal of Harbhajan & Co.