Question 1.
Solution:
Analysis:

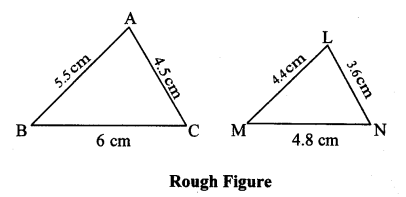
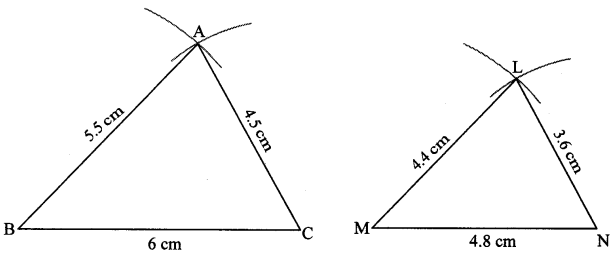
Question 2.
Solution:
Analysis:
As shown in the figure, Let R – P – L and R – Q – T.
∆PQR ~ ∆LTR … [Given]
∴ ∠PRQ ≅ ∠LRT … [Corresponding angles of similar triangles]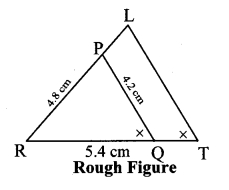

∴ sides of LTR are longer than corresponding sides of ∆PQR.
If seg QR is divided into 3 equal parts, then seg TR will be 4 times each part of seg QR.
So, if we construct ∆PQR, point T will be on side RQ, at a distance equal to 4 parts from R.
Now, point L is the point of intersection of ray RP and a line through T, parallel to PQ.
∆LTR is the required triangle similar to ∆PQR.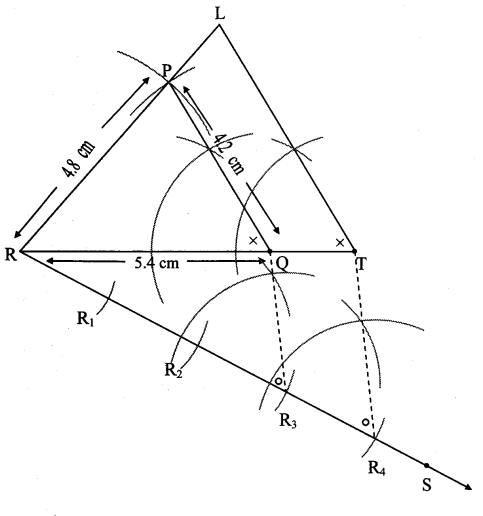
Steps of construction:
i. Draw ∆PQR of given measure. Draw ray RS making an acute angle with side RQ.
ii. Taking convenient distance on the compass, mark 4 points R1, R2, R3, and R4, such that RR1 = R1R2 = R2R3 = R3R4.
iii. Join R3Q. Draw line parallel to R3Q through R4 to intersects ray RQ at T.
iv. Draw a line parallel to side PQ through T. Name the point of intersection of this line and ray RP as L.
∆LTR is the required triangle similar to ∆PQR.
Question 3.
Solution:
Analysis:
∆RST ~ ∆XYZ … [Given]
∴ ∠RST ≅ ∠XYZ = 40° … [Corresponding angles of similar triangles]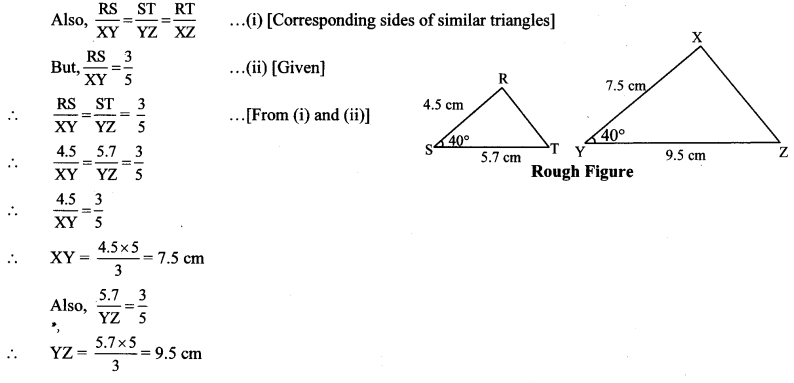

Question 4.
Solution:
Analysis:
As shown in the figure,
Let A – H – M and A – E – T.
∆AMT ~ ∆AHE … [Given]
∴ ∠TAM ≅ ∠EAH … [Corresponding angles of similar triangles]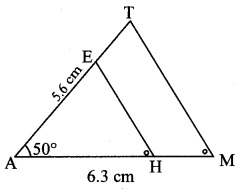

∴ Sides of AAMT are longer than corresponding sides of ∆AHE.
∴ The length of side AH will be equal to 5 parts out of 7 equal parts of side AM.
So, if we construct AAMT, point H will be on side AM, at a distance equal to 5 parts from A.
Now, point E is the point of intersection of ray AT and a line through H, parallel to MT.
∆AHE is the required triangle similar to ∆AMT.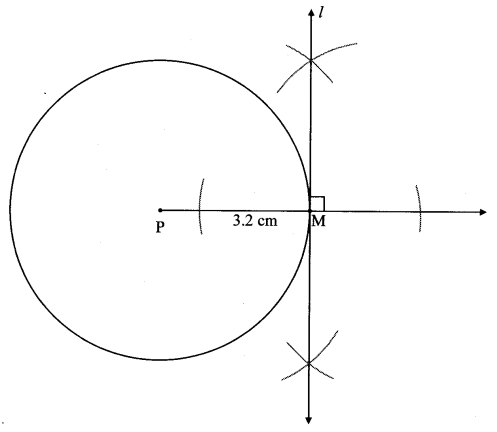
Steps of construction:
i. Draw ∆AMT of given measure. Draw ray AB making an acute angle with side AM.
ii. Taking convenient distance on the compass, mark 7 points A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, Ag and A7, such that
AA1 = A1A2 = A2A3 = A3A4 = A4A5 = A5A6 = A6A7.
iii. Join A7M. Draw line parallel to A7M through A5 to intersects seg AM at H.
iv. Draw a line parallel to side TM through H. Name the point of intersection of this line and seg AT as E.
∆AHE is the required triangle similar to ∆AMT.
Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
If length of side AB is 11.6/3 cm, then by dividing the line segment of length 11.6 cm in three equal parts, draw segment AB. (Textbook pg. no. 93)
Solution: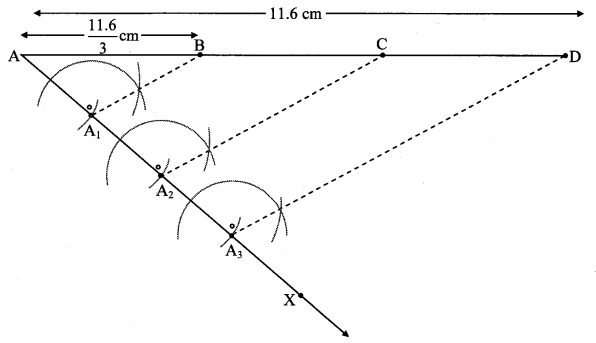
Steps of construction:
i. Draw seg AD of 11.6 cm.
ii. Draw ray AX such that ∠DAX is an acute angle.
iii. Locate points A1, A2 and A3 on ray AX such that AA1 = A1A2 = A2A3
iv. Join A3D.
v. Through A1, A2 draw lines parallel to A3D intersecting AD at B and C, wherein
AB = 11.6/3 cm
Question 2.
Construct any ∆ABC. Construct ∆ A’BC’ such that AB : A’B = 5:3 and ∆ ABC ~ ∆ A’BC’. (Textbook pg. no. 93)
Analysis:
As shown in the figure,
Let B – A’ – A and B – C’ -C
∆ ABC – A’BC’ … [Given]
∴ ∠ABC ≅ ∠A’BC’ …[Corresponding angles of similar trianglesi
∴ Sides of ∆ABC are longer than corresponding sides of ∆A’BC’. Rough figure
∴ the length of side BC’ will be equal to 3 parts out of 5 equal parts of side BC.
So if we construct ∆ABC, point C’ will be on side BC, at a distance equal to 3 parts from B.
Now A’ is the point of intersection of AB and a line through C’, parallel to CA.
Solution:
Let ∆ABC be any triangle constructed such that AB = 7 cm, BC = 7 cm and AC = 6 cm.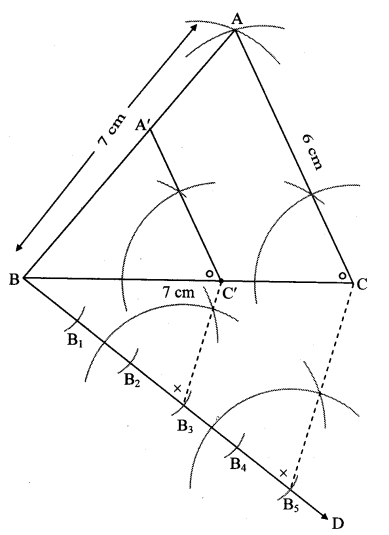
Question 3.
Construct any ∆ABC. Construct ∆A’BC’ such that AB: A’B = 5:3 and ∆ABC ~ ∆A’BC’.
∆A’BC’ can also be constructed as shown in the adjoining figure. What changes do we have to make in steps of construction in that case? (Textbook pg. no. 94)
Solution:
Let ∆ABC be any triangle constructed such that AB = 5cm,
BC = 5.5 cm and AC = 6 cm.
i. Steps of construction:
Construct ∆ABC, extend rays AB and CB.
Draw line BM making an acute angle with side AB.
Mark 5 points B1, B2, B3, B4, B5 starting from B at equal distance.
Join B3C” (ie 3rd part)
Draw a line parallel to AB5 through B3 to intersect line AB at C”
Draw a line parallel to AC through C” to intersect line BC at A”
ii. Extra construction:
With radius BC” cut an arc on extended ray CB at C’ [C’ – B – C]
With radius BA” cut an arc on extended ray AB at A’ [A’ – B – A]
∆A’BC’ is the required triangle.
