Question 1.
Obtain the differential equation by eliminating the arbitrary constants from the following equations:
Differentiating again w.r.t. x, we get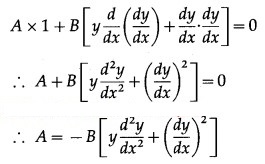
Substituting the value of A in (1), we get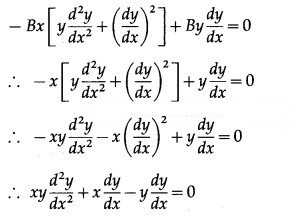
This is the required D.E.
Alternative Method: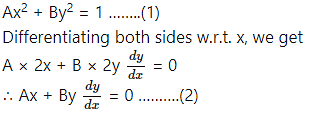
Differentiating again w.r.t. x, we get,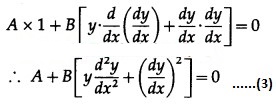
The equations (1), (2) and (3) are consistent in A and B.
∴ determinant of their consistency is zero.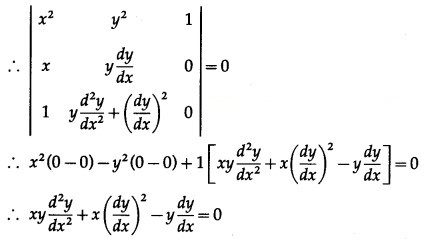
This is the required D.E.
(iii) y = A cos(log x) + B sin(log x)
Solution:
y = A cos(log x) + B sin (log x) ……. (1)
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
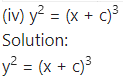
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get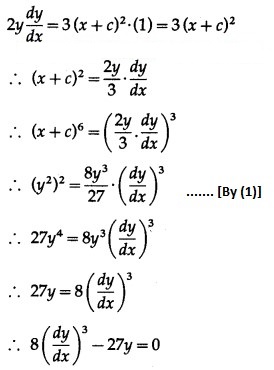
This is the required D.E.
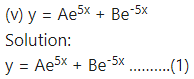
Differentiating twice w.r.t. x, we get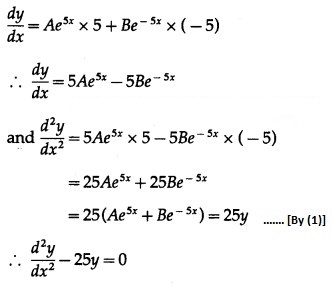
This is the required D.E.
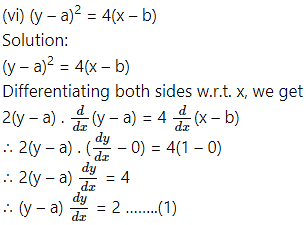
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get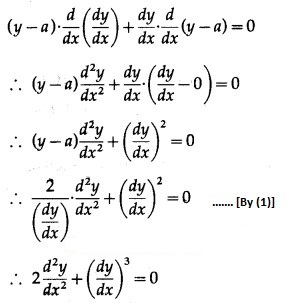
This is the required D.E.
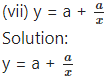
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
Substituting the value of a in (1), we get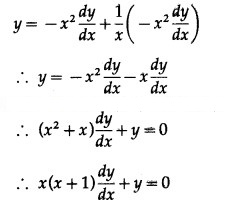
This is the required D.E.
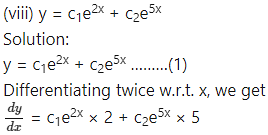
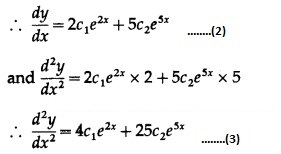
The equations (1), (2) and (3) are consistent in c1e2x and c2e5x
∴ determinant of their consistency is zero.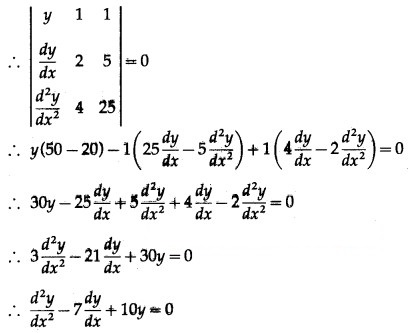
This is the required D.E.
Alternative Method: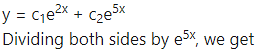
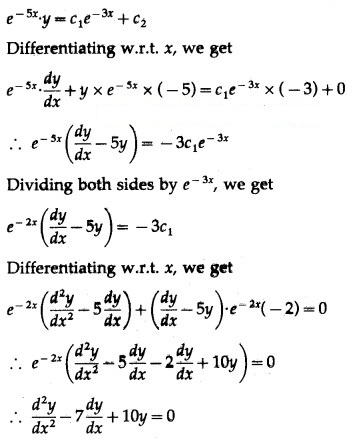
This is the required D.E.
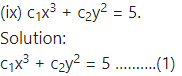
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get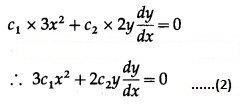
Differentiating again w.r.t. x, we get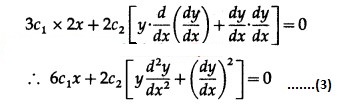
The equations (1), (2) and (3) in c1, c2 are consistent.
∴ determinant of their consistency is zero.
This is the required D.E.
(x) y = (A cos x + B sin x)
Solution:
y = (A cos x + B sin x)
∴ . y = A cos x + B sin x ………(1)
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get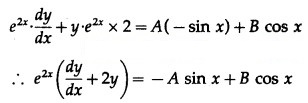
Differentiating again w.r.t. x, we get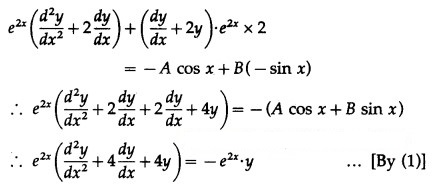
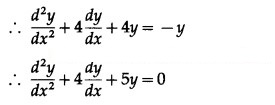
This is the required D.E.
Question 2.
Form the differential equation of family of lines having intercepts a and b on the coordinate axes respectively.
Solution:
The equation of the line having intercepts a and b on the coordinate axes respectively, is![]()
where a and b are arbitrary constants.
[For different values of a and b, we get, different lines. Hence (1) is the equation of family of lines.]
Differentiating (1) w.r.t. x, we get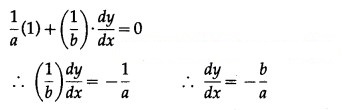
Differentiating again w.r.t. x, we get d2ydx2=0
This is the required D.E.
Question 3.
Find the differential equation all parabolas having length of latus rectum 4a and axis is parallel to the X-axis.
Solution:
Let A(h, k) be the vertex of the parabola whose length of latus rectum is 4a.
Then the equation of the parabola is (y – k = 4a (x – h), where h and k are arbitrary constants.
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get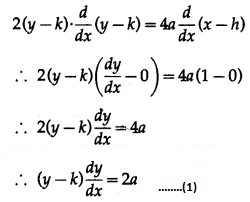
Differentiating again w.r.t. x, we get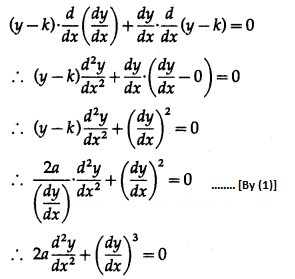
This is the required D.E.
Question 4.
Find the differential equation of the ellipse whose major axis is twice its minor axis.
Solution:
Let 2a and 2b be lengths of major axis and minor axis of the ellipse.
Then 2a = 2(2b)
∴ a = 2b
∴ equation of the ellipse is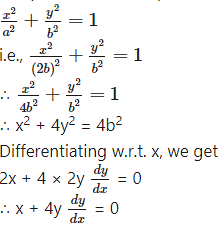
This is the required D.E.
Question 5.
Form the differential equation of family of lines parallel to the line 2x + 3y + 4 = 0.
Solution:
The equation of the line parallel to the line 2x + 3y + 4 = 0 is 2x + 3y + c = 0, where c is an arbitrary constant.
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get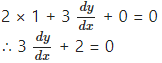
This is the required D.E.
Question 6.
Find the differential equation of all circles having radius 9 and centre at point (h, k).
Solution:
Equation of the circle having radius 9 and centre at point (h, k) is![]()
where h and k are arbitrary constant.
Differentiating (1) w.r.t. x, we get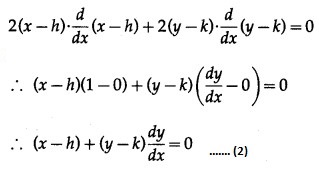
Differentiating again w.r.t. x, we get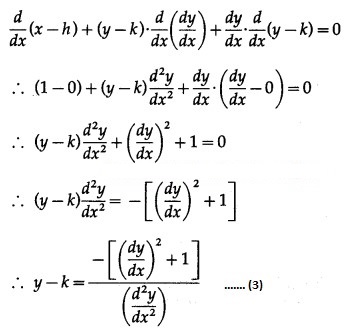
![]()
Substituting the value of (x – h) in (1), we get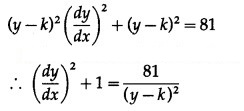
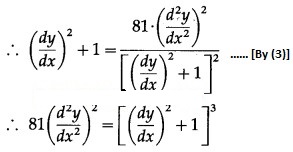
This is the required D.E.
Question 7.
Form the differential equation of all parabolas whose axis is the X-axis.
Solution: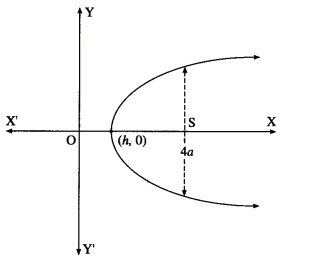
The equation of the parbola whose axis is the X-axis is
Differentiating again w.r.t. x, we get
This is the required D.E.
