Question 1.
Solution:

Question 2.
The vector equation of line 2x – 1 = 3y + 2 = z – 2 is
Solution:![]()
Question 3.
The direction ratios of the line which is perpendicular to the two lines
(A) 4, 5, 7
(B) 4, -5, 7
(C) 4, -5, -7
(D) -4, 5, 8
Solution:
(A) 4, 5, 7
Question 4.
Question 5.
Question 6.
(A) k = 1 or -1
(B) k = 0 or -3
(C) k = + 3
(D) k = 0 or -1
Solution:
(B ) k = 0 or -3
Question 7.![]()
(A) perpendicular
(B) inrersecting
(C) skew
(D) coincident
Solution:
(B) inrersecting
Question 8.
Equation of X-axis is
(A) x = y = z
(B) y = z
(C) y = 0, z = 0
(D) x = 0, y = 0
Solution:
(C) y = 0, z = 0
Question 9.
The angle between the lines 2x = 3y = -z and 6x = -y = -4z is
(A ) 45º
(B ) 30º
(C ) 0º
(D ) 90º
Solution:
(D ) 90º
Question 10.
The direction ratios of the line 3x + 1 = 6y – 2 = 1 – z are
(A ) 2, 1, 6
(B ) 2, 1, -6
(C ) 2, -1, 6
(D ) -2, 1, 6
Solution:
(B ) 2, 1, -6
Question 11.
Solution:
(A ) 14
Question 12.
Question 13.
Solution:![]()
Question 14.
The equation of the plane passing through (2, -1, 3) and making equal intercepts on the coordinate axes is
(A ) x + y + z =1
(B ) x + y + z = 2
(C ) x + y + z = 3
(D ) x + y + z = 4
Solution:
(D ) x + y + z = 4
Question 15.
Measure of angle between the planes 5x – 2y + 3z – 7 = 0 and 15x – 6y + 9z + 5 = 0 is
(A ) 0º
(B ) 30º
(C ) 45º
(D ) 90º
Solution:
(A ) 0º
Question 16.
The direction cosines of the normal to the plane 2x – y + 2z = 3 are
Solution:
Question 17.
The equation of the plane passing through the points (1, -1, 1), (3, 2, 4) and parallel to Y-axis is :
(A ) 3x + 2z – 1 = 0
(B ) 3x – 2z = 1
(C ) 3x + 2z + 1 = 0
(D ) 3x + 2z = 2
Solution:
(B ) 3x – 2z = 1
Question 18.
(A ) 17x – 47y – 24z + 172 = 0
(B ) 17x + 47y – 24z + 172 = 0
(C ) 17x + 47y + 24z +172 = 0
(D ) 17x – 47y + 24z + 172 = 0
Solution:
(A ) 17x – 47y – 24z + 172 = 0
Question 19.
(A ) 5
(B ) 3
(C ) 2
(D ) -5
Solution:
(A ) 5
Question 20.
The foot of perpendicular drawn from the point (0,0,0) to the plane is (4, -2, -5) then the equation of the plane is
(A ) 4x + y + 5z = 14
(B ) 4x – 2y – 5z = 45
(C ) x – 2y – 5z = 10
(D ) 4x + y + 6z = 11
Solution:
(B ) 4x – 2y – 5z = 45
II. Solve the following :
Question 1.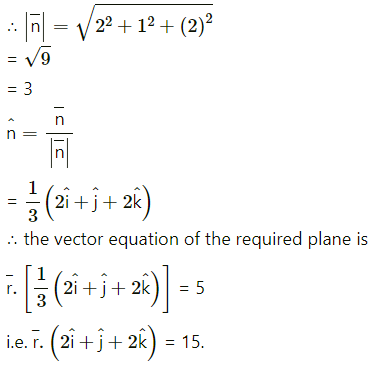
Question 2.
Find the perpendicular distance of the origin from the plane 6x + 2y + 3z – 7 = 0
Solution:
The distance of the point (x1, y1, z1) from the plane ax + by + cz + d is
![]()
∴ the distance of the point (1, 1, -1) from the plane 6x + 2y + 3z – 7 = 0 is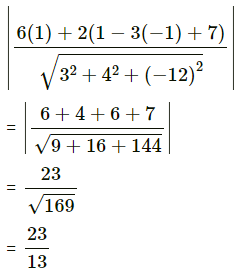
= 1units.
Question 3.
Find the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the plane 2x + 3y + 6z = 49.
Solution:
The equation of the plane is 2x + 3y + 6z = 49
Dividing each term by
and length of perpendicular from origin to the plane is p = 7.
the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from the origin to the plane are
(lp, ∓, np)i.e.(2, 3, 6)
Question 4.

This is the normal form of the equation of plane.
Question 5.
Find the vector equation of the plane passing through the points A(1, -2, 1), B (2, -1, -3) and C (0, 1, 5).
Solution:
The vector equation of the plane passing through three non-collinear points
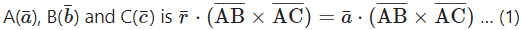

Question 6.
Find the Cartesian equation of the plane passing through A(1, -2, 3) and the direction ratios of whose normal are 0, 2, 0.
Solution:
The Cartesian equation of the plane passing through (x1, y1, z1), the direction ratios of whose normal are a, b, c, is
a(x – x1) + b(y – y1) + c(z – z1) = 0
∴ the cartesian equation of the required plane is
o(x + 1) + 2(y + 2) + 5(z – 3) = 0
i.e. 0 + 2y – 4 + 10z – 15 = 0
i.e. y + 2 = 0.
Question 7.
Find the Cartesian equation of the plane passing through A(7, 8, 6) and parallel to the plane
Solution: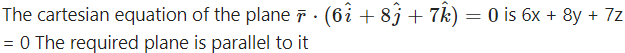
∴ its cartesian equation is
6x + 8y + 7z = p …(1)
A (7, 8, 6) lies on it and hence satisfies its equation
∴ (6)(7) + (8)(8) + (7)(6) = p
i.e., p = 42 + 64 + 42 = 148.
∴ from (1), the cartesian equation of the required plane is 6x + 8y + 7z = 148.
Question 8.
The foot of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to a plane is M(1, 2,0). Find the vector equation of the plane.
Solution:
Question 9.
The required plane makes intercepts 1, 1, 1 on the coordinate axes.
∴ it passes through the three non collinear points A = (1, 0, 0), B = (0, 1, 0), C = (0, , 1)

Question 10.
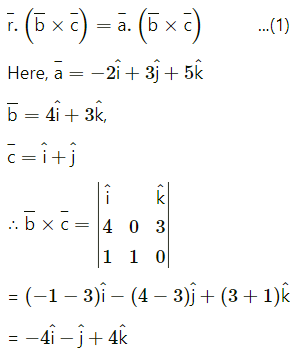
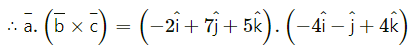
= (-2)(-4) + (7)(-1) + (5)(4)
= 8 – 7 + 8
= 35
∴ From (1), the vector equation of the required plane is

Question 11.


Question 12.
Find the vector equations of planes which pass through A(1, 2, 3), B (3, 2, 1) and make equal intercepts on the co-ordinates axes.
Question is modified
Find the cartesian equations of the planes which pass through A(1, 2, 3), B(3, 2, 1) and make equal intercepts on the coordinate axes.
Solution:
Case 1 : Let all the intercepts be 0.
Then the plane passes through the origin.
Then the cartesian equation of the plane is
ax + by + cz = 0 …..(1)
(1, 2, 3) and (3, 2, 1) lie on the plane.
∴ a + 2b + 3c = 0 and 3a + 2b + c = 0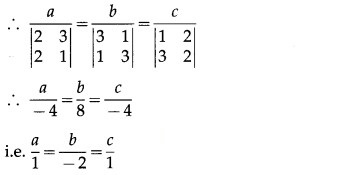
∴ a, b, c are proportional to 1, -2, 1
∴ from (1), the required cartesian equation is x – 2y + z = 0.
Case 2 : Let the plane make non zero intercept p on each axis.![]()
i.e. x + y + z = p …(2)
Since this plane pass through (1, 2, 3) and (3, 2, 1)
∴ 1 + 2 + 3 = p and 3 + 2 + 1 = p
∴ p = 6
∴ from (2), the required cartesian equation is
x + y + z = 6
Hence, the cartesian equations of required planes are x + y + z = 6 and x – 2y + z = 0.
Question 13.
Find the vector equation of the plane which makes equal non-zero intercepts on the co-ordinates axes and passes through (1, 1, 1).
Solution:
Case 1 : Let all the intercepts be 0.
Then the plane passes through the origin.
Then the vector equation of the plane is ax + by + cz …(1)
(1, 1, 1) lie on the plane.
∴ 1a + 1b + 1c = 0
∴ from (1), the required cartesian equation is x – y + z = 0
Case 2 : Let he plane make non zero intercept p on each axis.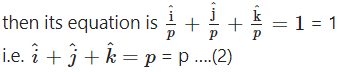
Since this plane pass through (1, 1, 1)
∴ 1 + 1 + 1 = p
∴ p = 3
Question 14.
Solution:
The acute angle between the planes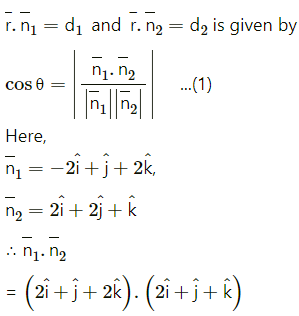
= (1)(2) + (1)(1) + (2)(1)
= 2 + 1 + 2
= 5
Also,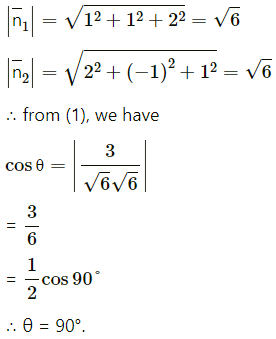
Question 15.

= (2)(2) + (3)(-1) + (-6)(1)
= 4 – 3 – 6
= -5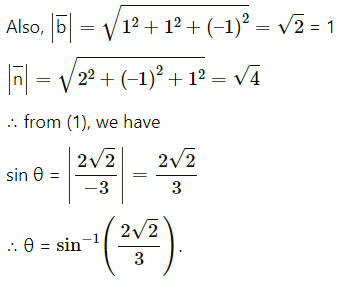
Question 16.
Solution:
Question 17.
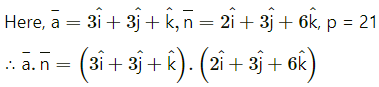
= (3)(2) + (3)(3) + (1)(-6)
= 6 + 9 – 6
= 9
Question 18.
Find the distance of the point (13, 13, -13) from the plane 3x + 4y – 12z = 0.
Solution: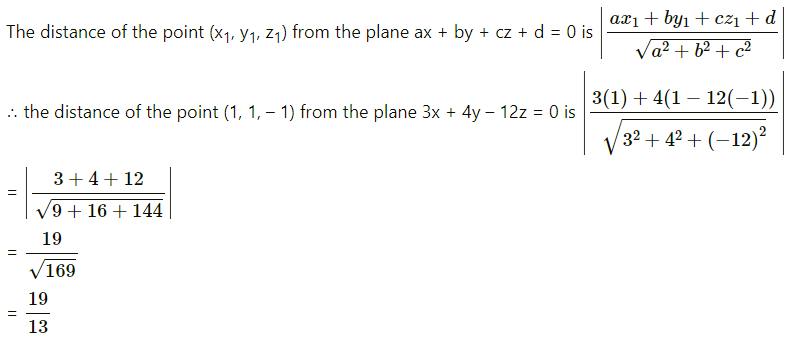
= 19units.
Question 19.

Question 20.
Find the vector equation of the plane which bisects the segment joining A(2, 3, 6) and B( 4, 3, -2) at right angle.
Solution:


Question 21.
Show thatlines x = y, z = 0 and x + y = 0, z = 0 intersect each other. Find the vector equation of the plane determined by them.
Solution:
Given lines are x = y, z = 0 and x + y = 0, z = 0.
It is clear that (0, 0, 0) satisfies both the equations.
∴ the lines intersect at O whose position vector is 0¯¯¯
Since z = 0 for both the lines, both the lines lie in XY- plane.
Hence, we have to find equation of XY-plane.
Z-axis is perpendicular to XY-plane.
