Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Find my match!
Question a.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Lotus | a. Flower and leaves attract insects |
| 2. Aloe | b. Haustorial roots for absoption of food |
| 3. Cuscuta | c. Adapted to live in deserts |
| 4. Venus fly trap | d. Adapted to live in water |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Lotus | d. Adapted to live in water |
| 2. Aloe | c. Adapted to live in deserts |
| 3. Cuscuta | b. Haustorial roots for absoption of food |
| 4. Venus fly trap | a. Flower and leaves attract insects |
2. Read the paragraph and answer the following questions:
I am a penguin. I live in polar region covered by snow. My abdomen is white. My skin is thick with a layer of fat underneath. My body is spindle-shaped. My wings are small. My toes are webbed. We live in flocks.
Question a.
Why is my skin white and thick and why is there a thick layer of fat underneath?
Answer:
- White skin colour camouflage with the snow so penguins cannot be easily spotted and they get protected from enemies.
- Thick skin and thick layer of fat underneath gives them protection from severe cold.
Question b.
Why do we live in flocks sticking close to each other?
Answer:
Penguins live in flocks sticking close to each other because sticking close to each other reduce the relative area so there is least loss of heat and they get protection from cold.
Question c.
Which geographical region do I inhabit? Why?
Answer:
- Penguins inhabit Antarctica region. Antarctica is surrounded by ocean. Climate is colder, drier and windier.
- It does not have human population. This climate is suitable for penguins, so they inhabit Antarctica.
Question d.
Which adaptations should you have to enable you to live permanently in the polar region? Why?
Answer:
- I should be a warm blooded animal. This should allow me to permanently live in polar region.
- My body has to be covered with thick fur or scale so that loss of heat will be very less and I can survive in severe cold.
3. Who is lying?
Question a.
Cockroach – I have five legs.
Answer:
Cockroach is lying. It has six legs.
Question b.
Hen – My toes are webbed.
Answer:
Hen is lying because hen’s toes are not webbed. Duck has webbed toes.
Question c.
Cactus – My fleshy, green part is a leaf.
Answer:
Cactus is lying. It’s fleshy, green part is a stem not a leaf.
4. Read each of the following statements. Write a paragraph about adaptation with reference to each statement.
Question a.
There is extreme heat in deserts.
Answer:
- Plant’s stem is fleshy, leaves get modified into thorns to reduce loss of water. Steam perform photosynthesis in the absence of leaves.
- Animals have cushioned soles, hump, long legs and nostrils are protected by folds of skin. Eyelashes are long and thick.
Question b.
Grasslands are lush green.
Answer:
Insects like grasshoppers have green colour so they can be camouflaged amidst grasses.
Question c.
We hide.
Answer:
In equatorial region grasses are very tall, so to protect themselves animals like tiger, elephants and deer remain hidden in these tall grasses.
Question d.
We have long ears.
Answer:
It helps the animals to receive sounds from long distance, and they can protect themselves from predators.
5. Answer the following:
Question a.
Why is the camel called the ‘ship of the desert’?
Answer:
- Camel lives in a desert easily due to following adaptations. It has long legs and cushioned soles which keep the body of camel above the sand and cushioned soles do not allow to sink in sand while walking.
- The nostrils are protected by folds of skin.
- The eyelashes are long and thick.
- It has hump which stores fats so it helps camel to survive in desert for many days without food and water.
Due to above adaptations camel is used to carry people and transport goods from one place to another place in the desert. Therefore, camel is called the ship of the desert.
Question b.
How can the plants like cactus and acacia live in deserts with scarce water?
Answer:
The plants like cactus and acacia live in deserts with scarce water due to the following adaptations.
- Leaves are like small needles or have been modified into thorns, as a result they lose very little water by evaporation.
- The stem stores water and food so it is fleshy.
- The stems are green as they perform photosynthesis in the absence of leaves.
- Their roots penetrate deep into the soil in search of water.
- There is a thick layer of a waxy substance on the stems.
Question c.
What is the inter-relationship between adaptations of organisms and their surroundings?
Answer:
1. Adaptations of organisms depend on the changes in the surroundings.
2. To adjust with those changes in the surroundings adaptation takes place gradually and continuously in organisms.
3. Changes that take place in the various organs and life processes of organisms, enable them to live, feed, reproduce to perpetuate themselves and to protect themselves from their enemies in specific surroundings, depending upon the habitat and its geographical conditions, are called adaptations.
Question d.
How are organisms classified?
Answer:
- Different scientists have used different criteria and independently classified plants and animals.
- A hierarchy is formed in the classification that starts with kingdom Animalia or kingdom Plantae, further groups and sub-groups are formed depending upon basic similarities and differences.
- This is called the ‘hierarchy of classification’.
- Binomial nomenclature is used to identify each organism. Accordingly, a scientific name has been assigned to each organism.
- It consists of two parts – first part is ‘genus’ and second ‘species’.
- All identified organisms have been assigned a binomial name as per the guidelines of the International code of Nomenclature. For e.g.
| Genus | Species | |
| Mango | Mangifera | Indica |
| Human | Homo | Sapiens |
Activity:
Question 1.
Find out how the gradual adaptation from primitive man to modern man must have taken place.
Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
Leaves of some aquatic plants are …………. and …………. ike a ribbon.
Answer:
thin, slender
Question 2.
…………. in stems and …………. of aquatic plants are useful for floating in water.
Answer:
Air spaces, petioles
Question 3.
Leaves of desert plants are modified into …………. .
Answer:
thorns
Question 4.
The stems of desert plants are green as they perform …………. in the absence of leaves.
Answer:
photosynthesis
Question 5.
…………. roots of grasses prevent soil erosion.
Answer:
Fibrous
Question 6.
Grasses in the …………. region are very tall.
Answer:
equatorial
Question 7.
…………. are found in hilly areas as well as plains.
Answer:
Vast meadows
Question 8.
Plants need …………., …………. and …………. for growth.
Answer:
nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium
Question 9.
Dodder has …………. roots for absorbing nutrients from the host plant.
Answer:
haustorial (sucking)
Question 10.
Fungi do not have …………. so cannot perform photosynthesis.
Answer:
chlorophyll
Question 11.
Fish breathe with …………. instead of a nose.
Answer:
gills
Question 12.
Fish have …………. within the body to help them to float.
Answer:
air bladders
Question 13.
Frog and duck have …………. toes.
Answer:
webbed
Question 14.
Tigers have …………. paws.
Answer:
padded
Question 15.
Bats can fly with the help of …………. .
Answer:
patagium.
Question 16.
Desert plants are either leafless or their leaves are like …………. or modified into …………. .
Answer:
needles, thorns
Question 17.
Spring like …………. on the stems of some climbers are examples of their adaptation.
Answer:
Tendrils
Question 18.
…………. is not a sudden process, it is gradual and continuous.
Answer:
Adaptation
Question 19.
…………. proposed the theory of the survival of the fittest.
Answer:
Charles Darwin
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Cactus | a. Herbivorous animal |
| 2. Pine | b. Carnivorous animal |
| 3. Tiger | c. Snowy region plant |
| 4. Blackbuck | d. Desert plant |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Cactus | d. Desert plant |
| 2. Pine | c. Snowy region plant |
| 3. Tiger | b. Carnivorous animal |
| 4. Blackbuck | a. Herbivorous animal |
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Dog | a. Hibiscus roso sinensis |
| 2. Cow | b. Sorghum bicolor |
| 3. Hibiscus | c. Bos taurus |
| 4. Jowar | d. Canis lupus familiarise |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Dog | d. Canis lupus familiarise |
| 2. Cow | c. Bos taurus |
| 3. Hibiscus | a. Hibiscus roso sinensis |
| 4. Jowar | b. Sorghum bicolor |
Name the following:
Question 1.
Animals which live in desert in deep burrows.
Answer:
Rats, snakes, spiders, lizards
Question 2.
Animals which have webbed feet.
Answer:
Frog, duck
Question 3.
Plants of snowy regions.
Answer:
Deodar, pine
Question 4.
Plants that eat insects.
Answer:
Drosera, venus flytrap, pitcher plant
Question 5.
World Frog Protection Day.
Answer:
29th April
Question 6.
2 parts of bionomial nomenclature.
Answer:
genus and species.
Who am I?
Question 1.
My leaves trap insects.
Answer:
Venus fly trap or pitcher plant.
Question 2.
I have waxy feathers and webbed feet.
Answer:
Duck
Question 3.
I breath through skin in water and through lungs on land.
Answer:
Frog
Question 4.
I have sucking roots through which I take nutrition from my host plant.
Answer:
Dodder (cuscuta)
Question 5.
I have silvery white body with thick long hair
Answer:
Snow animals like polar bear.
Question 6.
I have waxy broad leaves and air spaces in my stem.
Answer:
Lotus (or aquatic plants)
Question 7.
My Scientific name is Bos taurus.
Answer:
Cow
Question 8.
I discovered Binomial nomenclature.
Answer:
Carl Linnaeus
Question 9.
I have special thin folds in between my forelegs and hind legs called patagium.
Answer:
Bat
Question 10.
I am mango, my genus is?
Answer:
Mangifera
Say whether true or false, correct and rewrite the false statements:
Question 1.
Killing or harming frogs is prohibited by the Wild Life Protection Act.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Scientific name of jowar is Bos taurus.
Answer:
False. Scientific name of jowar is Sorghum bicolor
Question 3.
Theory of natural selection was found by Charles Darwin.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
T.V. Channels like National Geographic, Wild and Discovery show about the feeding habits of animals.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
The spindle shaped body of birds maximizes the resistance of air while flying.
Answer:
False. The spindle shaped body of birds minimises the resistance of air while flying.
Question 6.
House lizard and monitor lizards have webbed toes.
Answer:
False. House lizard and monitor lizards have clawed toes.
Question 7.
Crocodiles use their muscles for creeping.
Answer:
True
Question 8.
The eyes of predatory carnivores are located on either side of the head.
Answer:
False. The eyes of predatory carnivores are located in the front of their head.
Question 9.
A frog is an amphibian.
Answer:
True
Question 10.
Diverse types of bushes and grasses are found in the grasslands.
Answer:
True.
Complete the given table:
Question 1.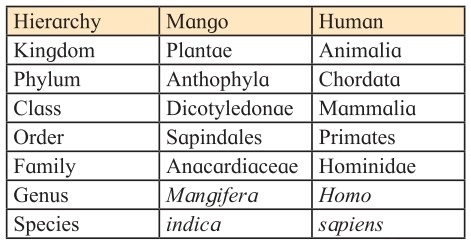
Question 2.
Give one special adaptation or features of the following plant or animal to suit its habitat surrounding
Answer:
| Plant/animal | Special adaptation/features |
| 1. Fish | Stream lined body |
| 2. Bird | Hollow bones, feathers |
| 3. Camel | Thick skin, folds in skin near nosetrils |
| 4. Deer | long and tapering legs with strong hooves |
| 5. Tiger | Padded paws, sharp canine teeth |
| 6. Duck | waxy feathers, webbed toes |
| 7. Fungi | Root like fibers |
| 8. Cuscuta | Leafless, yellow thread like stem with haustorial (sucking) roots |
| 9. Venus fly trap | Trigger hair inside their traps |
| 10. Deodar tree | Conical shape and needle shaped leaves |
| 11. Grape vine | Tendrils for support |
| 12. Acacia | Fleshy thick green stem with leaves turned into thorns. |
Who is lying?
Question 1.
Camel has thin skin and short eyelashes.
Answer:
Camel is lying – It has thick skin and long and thick eyelashes.
Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
What is called ‘hierarchy of classification’?
Answer:
- A hierarchy is formed in the classification that starts with kingdom Animalia or Kingdom Plantae, further groups and sub-groups are formed depending upon basic similarities and differences.
- This is called the ‘hierarchy of classification’.
Question 2.
What theories were proprosed by Charles Darwin
Answer:
The theories of Charles Darwin are Theory of natural selection and theory of survival of the fittest.
Question 3.
Explain the terms Autotrophic and Parasitic
Answer:
1. Plants which are able to produce their own food with the help of the process of photosynthesis are called autotrophic plants eg. All green plants.
2. Plants which are not able to produce their own food but depend upon other plants for their nutrition are called parasitic plants They are leafless and non green in colour eg. Dodder (cuscuta). They have haustorial (sucking) roots for absorbing nutrients from the host plant.
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
Leaves of some aquatic plants are thin and slender like a ribbon.
Answer:
Leaves of some aquatic plants are thin and slender like a ribbon because this shape helps them to withstand fast currents of water.
Question 2.
Some aquatic plants have air spaces in stems.
Answer:
Some aquatic plants have air spaces in stems because air spaces help the plants to float on water.
Question 3.
Desert plants have thorns.
Answer:
- Desert plants have thorns because in deserts, due to scarcity of water these plants are either leafless or their leaves are like small needles or modified into thorns.
- They lose very little water by evaporation due to little surface area. This helps plants to survive in desert.
Question 4.
Desert plants have green stem.
Answer:
Desert plants have green stem because green stem performs photosynthesis in the absence of leaves.
Question 5.
Desert plants have strong roots.
Answer:
Desert plants have strong roots so they can penetrate deep into the soil in search of water.
Question 6.
Deodar tree is conical in shape.
Answer:
Deodar tree grows in snowy region and conical shape of the tree doesn’t allow snow to accumulate on the tree and thus protect the tree from snow.
Question 7.
Pine tree has thick bark.
Answer:
Pine tree grows in snowy region where it is extremely cold and its thick bark helps the tree to withstand the cold.
Question 8.
Plants in forest grow tall.
Answer:
In forest region variety of trees, shrubs and herbs are found. These plants compete amongst themselves for sunlight. Hence trees grow tall to get sunlight.
Question 9.
Cuscuta has haustorial roots.
Answer:
- Cuscuta is a parasitic plant. It is leafless and cannot prepare food on its own.
- So to get food haustorial (sucking) roots penetrate up to the conducting vessels of the host plant to absorb water and food, the Cuscuta has haustorial roots.
Question 10.
Fungi have root-like fibers.
Answer:
- Fungi are parasitic.
- They do not have chlorophyll and cannot perform photosynthesis.
- So these root-like fibers help to absorb the food from the starchy foodstuffs like bhakri and bread.
Question 11.
Pitcher plant eats insects.
Answer:
- Pitcher plant grows in a soil where nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium are very less. But the plant needs these for the growth.
- So to fulfill the need for nitrogen, pitcher plant consumes insects.
Question 12.
Duck and frog have webbed feet.
Answer:
When duck and frog are in water at that time the webbed feet act as oars and help them to swim in water.
Question 13.
Frogs can swim easily in water.
Answer:
Frogs have webbed toes, slippery, smooth skin and triangular head. This helps the frog to swim easily through water.
Question 14.
Tiger has sharp and pointed canine teeth.
Answer:
Tiger is a carnivorous animal. So the sharp and pointed canine teeth help the tiger to tear the prey and eat.
Question 15.
Blackbuck has eyes on either side of the head.
Answer:
Blackbuck is a herbivore animal and eyes on either side of the head gives them wide angle vision which helps to protect themselves from predators.
Question 16.
Tigers have padded paws.
Answer:
Tigers are carnivorous animals. So these padded paws enable them to silently stalk their prey and capture it easily.
Question 17.
The eyes of predatory carnivores are located in the front of their head.
Answer:
The eyes of predatory carnivores are located in the front of their head because it helps them to spot their prey from a long distance.
Question 18.
Camel can live in desert.
Answer:
- Camel can live in desert because it has thick skin to prevent loss of water from the body. Their legs are long with flat and cushioned soles.
- The nostrils are protected by folds of skin. The eyelashes are long and thick so these adaptations enable Camels to live in desert easily.
Question 19.
White fox has white body colour.
Answer:
- White fox lives in snowy region which throughout the year is covered with snow.
- White colour of fox matches with the snow so it gets camouflaged in snow and it can save itself from predators.
Question 20.
Birds can fly in the air.
Answer:
- Birds can fly in the air because the spindle shaped body minimises the resistance of air while flying.
- Their hollow bones, body covering of feathers and forelegs being modified into wings, their body being light in weight, all these factors make the birds adapted to fly in the air.
Can you tell?
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Arc the plants and animals from Kashmir and Rajasthan of the same type? Can you elaborate on any differences between the two?
Answer:
Plants and animals from Kashmir and Rajasthan are of different types.
Differences in plants:
- Plants of Kashmir, which is a snowy region, are conical in shape due to their sloping branches.
- This shape prevents the snow accumulation on the tree and the thick bark helps the tree to withstand the cold.
- But the plants of Rajasthan, which is a desert region, are either leafless or their leaves are small, needle shaped or have been modified into thorns. So the loss of water can be reduced
- The stem stores water and food so they are fleshy. The stem performs photosynthesis in the absence of leaves.
Differences in animals:
- Animals of Kashmir have thick hair and white or silver body colour camouflaged with snow. This helps them to get protection in snowy region.
- The animals of Rajasthan have long legs with flat and cushioned soles.
- The nostrils are protected by folds of skin. The eyelashes are long and thick. It gives protection from sand and heat.
Question 2.
In what way are sloping branches useful to plants in a snowy region?
Answer:
In a snowy region sloping branches of a plant gives conical shape to the tree and it doesn’t allow snow to accumulate on tree inspite of heavy snowfall and thus protect the tree from severe cold and snow.
Question 3.
What is the main difference between vehicles on the road and aeroplanes?
Answer:
The two main differences between vehicles on the road and aeroplanes are:
- aeroplanes have wings whereas vehicles on the road do not have wings.
- The body of aeroplanes are spindle shaped and the body of vehicles on the road depends on the number of wheels they have.
Use your brain power!
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Why does water trickle off lotus leaves?
Answer:
- Water trickles off lotus leaves because it is coated with waxy covering on it.
- It is one of the adaptations of aquatic plants to survive in water without getting wet and rot or sink to the bottom.
Question 2.
Why don’t the leaves of lotus plants rotinwatei?
Answer:
leaves of these plants do not rot in water because it is covered with waxy coating on it so that they do not get wet.
Question 3.
Why are roots of lotus plants short and fibrous?
Answer: –
- These plants grow in water so the roots do not need to go deep down in search of water. Their roots are not anchored in the soil.
- So their roots are short and fibrous.
Question 4.
The lotus stalk has holes or air spaces?
Answer:
- The air spaces in stems and petioles of aquatic plants are useful for making them float in water and also to prevent them from rotting
- Hence, the lotus stalk has holes or air spaces.
Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Explain the Darwin’s theory of evolution.
Answer:
Charles Darwin, a biologist suggested two principles in his theory of evolution.
- Theory of survival of the fittest: He said that only those organisms are likely to survive which can best adapt themselves to a changing environment. This is called the theory of survival of the fittest.
- Theory of ‘Natural selection’: If an organism is bom with a new beneficial characteristic and is able to survive, this change is preserved in the next generation. This is called the theory of ‘natural selection’.
Diagram based questions:
Draw a neat labelled diagram of fish and answer the following questions.
Answer: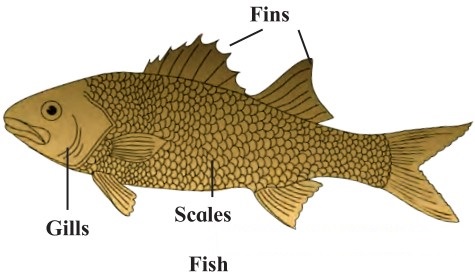
Question a.
Why do fish have a body tapering towards both its ends?
Answer:
Fish have its body tapering towards its ends, to allow them to swim with least resistance in water.
Question b.
Why do Fish have transparent eyelids.
Answer:
The transparent eyelids of fish protect the eyes from the substance in the water
Question c.
How are they able to float?
Answer:
Fish have air bladders within their body which help them to float.
Observe the diagram and answer the questions.
Answer:
Question a.
What habitat does this camel live in?
Answer:
Camel lives in desert habitats or in areas where there is scarcity of water.
Question b.
State any 2 of its body adaptations to survive in desert?
Answer:
- Thick skin to prevent loss of water from the body
- The eyelashes are long and thin
- Their legs are long and flat with cushioned soles
Question c.
How does a camel protect itself from sand storms or winds carrying sand?
Answer:
Camels have nostrils protected by folds of skin and long thick eyelashes to prevent entry of fir dust and sand into its nose and eyes.
Paragraph based questions:
Compare and contrast:
Question 1.
Compare the lotus plant to the Acacia plant and Hibiscus plant.
Answer:
| Lotus plant | Hibiscus plant | Acacia plant |
| I. Stem have air spaces in them | Stem do not have air spaces and do not store too much of water and food | Stem is fleshy and stores water and food |
| ii. Leaves have a waxy coating | Leaves do not have a waxy coating and have thin lamina | Leaves are not present and if present are very tiny or modified into thorns |
Question 2.
What is the difference between the plants given in the pictures. Give 2 points of difference taking into consideration their adaptations with their surroundings.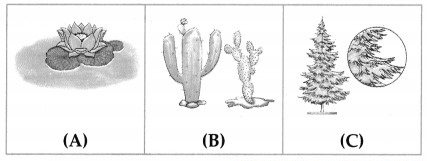
Answer:
| A. Cactus | B. Lotus | C. Deodar tree |
| i. Stem is green and fleshy | Stem is with air space | Shape of tree is conical |
| ii. leaves are reduced or absent and replaced by thorns | Leaves are broad and with a waxy coating | Leaves are needle shaped |
Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board: In the state of Maharashtra, the Science curriculum for Class 7 is divided into several chapters, each focusing on different aspects of scientific knowledge and inquiry. Chapter 1 lays the foundation for scientific thinking and introduces students to the basic concepts and principles of science.
Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board is designed to develop critical thinking skills and a scientific mindset among students, allowing them to explore the world around them and make observations and inferences based on evidence.
In this blog post, we will delve into Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board curriculum, discussing its key topics and providing valuable insights for students and educators alike.
Download Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board
Understanding the first chapter of the Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board curriculum is crucial for students as it sets the foundation for their scientific knowledge and thinking skills. This chapter introduces students to the basic concepts and principles of science, helping them develop a scientific mindset and the ability to think critically.
By grasping the fundamental ideas presented in this chapter, students will be better equipped to navigate through the rest of the Science curriculum and comprehend more complex topics in later chapters.
Furthermore, the skills and knowledge gained through studying Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board will not only benefit students in their academic journey but also their everyday lives. They will be able to apply scientific thinking to analyze and solve problems, make informed decisions, and better understand the world around them.
Therefore, both students and educators must dedicate ample time and effort to thoroughly comprehend and master the content of this chapter. So, let’s dive into the key topics of Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board and explore the valuable insights it has to offer.
Key concepts covered in Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board
In Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board, students will be introduced to several key concepts that form the basis of scientific understanding. These concepts include the study of living organisms, their classification, and the diversity of life forms on Earth.
One of the core topics covered in this chapter is the classification of living organisms. Students will learn about the various criteria used to classify organisms into different groups, including their physical characteristics, habitats, and modes of nutrition. They will also explore the importance of classification in organizing and studying the vast array of living things on our planet.
Download Class 7th Other Books PDF
Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Hindi Book
Maharashtra Board English Balbharati Std 6 Textbook PDF
Maharashtra State Board Std 6 Geography Textbook PDF
Maharashtra State Board 6th Standard English Textbook PDF
Maharashtra Board Std 6th Maths Textbook PDF
Maharashtra Board 6th Std Science Textbook Download PDF
Maharashtra State Board Class 6 History Book
Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Civics Book
Another important concept covered in Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board is the diversity of life forms. Students will gain an understanding of the immense variety of living organisms on Earth and how they have adapted to different environments over time. They will explore the concept of biodiversity and its significance in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Additionally, students will learn about the basic structure and functions of cells, the building blocks of life. They will delve into topics such as cell organization, cell division, and the concept of a cell as the fundamental unit of life.
By understanding these key concepts from Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board, students will develop a solid foundation for future scientific learning and exploration. In the next section, we will delve deeper into each of these concepts and explore their significance in greater detail. So, let’s embark on this exciting journey of discovery and expand our scientific knowledge together.
Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer Maharashtra Board Pdf
Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer Maharashtra Board Pdf, Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer Maharashtra Board Pdf, Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer Maharashtra Board Pdf.
Resources for studying Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board
In order to effectively study and understand Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board, it is important to have the right resources at your disposal. Here are a few recommendations to enhance your learning experience:
1. Textbook: Make sure you have the official Maharashtra Board Class 7 Science textbook for a comprehensive understanding of the concepts discussed in Chapter 1. Familiarize yourself with the content and refer back to it whenever necessary.
2. Online resources: There are many websites and online platforms that provide additional resources for studying Chapter 1. Look for websites that offer interactive activities, quizzes, and videos to reinforce your understanding of the topics.
3. Reference books: If you require more in-depth explanations or examples, consider referring to supplementary reference books on Class 7 Science. These books can provide further clarity and expand your knowledge of the concepts covered in Chapter 1.
4. Study guides: Look for study guides specifically tailored for Class 7 Science Maharashtra Board Chapter 1. These guides often summarize the content and provide practice questions to test your comprehension.
By utilizing these resources, you will be well-equipped to tackle the concepts discussed in Chapter 1 of Class 7 Science. Remember to stay organized, set a study schedule, and ask for help whenever needed. Good luck with your studies.
Maharashtra Board Class 7th Books Solution
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Science Solutions
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 7 Civics
Maharashtra State Board Solutions Class 7
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 History Solutions
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 7 Marathi
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 7 History
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 7 Hindi
Maharashtra Board Solutions Class 7 Geography
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Maths Solutions
Maharashtra State Board Class 7 English Solutions
Overview of the Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board content
Next, let’s provide an overview of the content covered in Chapter 1 of Class 7 Science in Maharashtra Board. This chapter titled “Nutrition in Plants” focuses on understanding the various modes of nutrition in plants and how they obtain their food.
The Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board begins by introducing the concept of autotrophic nutrition and the process of photosynthesis. It explains how plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, water, and chlorophyll to produce glucose and oxygen. The importance of chlorophyll and the photosynthetic organs of plants are also discussed.
Next, the Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board explores heterotrophic nutrition in plants. It explains how plants that are unable to synthesize their food obtain nutrients from external sources through various methods like parasitic, saprophytic, and insectivorous modes of nutrition.
Furthermore, the chapter delves into the process of nutrition in non-green plants and provides examples of different modes of nutrition found in these plants.
Overall, Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board provides a comprehensive understanding of the nutrition in plants, detailing both autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition. Studying this chapter will lay a strong foundation for further discussions on plant biology and ecology.
Tips for effective studying Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board
When studying Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board, it is important to adopt effective study strategies to enhance your understanding of the subject matter. Here are a few tips to help you study more efficiently:
1. Read the chapter thoroughly: Start by reading the chapter multiple times to get familiar with the content. Pay close attention to key concepts, definitions, and examples provided.
2. Highlight important points: Use highlighters or underline key information in your textbook. This will help you quickly identify and review important concepts later.
3. Take notes: As you read, jot down important points in your own words. Summarize the information in a way that makes sense to you, as this will aid in retention.
4. Create flashcards: Make flashcards for key definitions and concepts. Use these cards to test your knowledge and review the material regularly.
5. Practice with sample questions: To reinforce your understanding, solve sample questions, and practice exercises provided at the end of the chapter. This will help you gauge your level of comprehension and identify any areas that require further clarification.
By following these tips and actively engaging with the material, you will be well-prepared to excel in your study of Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board.
Conclusion and final thoughts: Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board
:In conclusion, studying Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board requires a disciplined approach and effective study strategies. By following the tips mentioned above, you can enhance your understanding of the subject and have a more productive study session.
Remember that simply reading the Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board is not enough; you need to actively engage with the content. Highlighting important points, taking notes, creating flashcards, and practicing with sample questions are all valuable techniques that can help improve your comprehension and retention.
Additionally, it is essential to allocate regular study time and avoid cramming before exams. By consistently reviewing the material and seeking clarification for any doubts, you can build a strong foundation in Class 7 Science.
With these strategies in your arsenal, you will be well-equipped to excel in your study of Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Maharashtra Board. Keep up the hard work, and best of luck in your academic pursuits!
