Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the blanks with the right word from the brackets:
Question a.
The process of digestion starts from the ………….. (stomach, mouth).
Answer:
mouth
Question b.
Eyelids have …………… muscles. (voluntary, involuntary)
Answer:
involuntary
Question c.
……………. is not a function of muscular system. (production of blood cell, performing movement)
Answer:
Production of blood cells
Question d.
Muscles of the heart are …………….. . (ordinary muscles, cardiac muscles)
Answer:
cardiac muscles
Question e.
Pushing forward the food that has been chewed is the function of the …………… . (stomach, oesophagus)
Answer:
Oesophagus.
2. Find a match for me.
Question a.
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Cardiac muscle | a. Always functions in pairs |
| 2. Are brought about by muscle | b. We never feel tired |
| 3. Pepsin | c. Uncontrolled and painful contraction of muscles |
| 4. Cramps | d. Chewing movement of the jaw |
| 5. Skeletal muscles | e. Enzymes of the gastric juice |
3. Who is telling a lie?
Question a.
| Organ | Statement |
| 1. Tongue | a. My taste buds can tell only a sweet taste. |
| 2. Liver | b. I am the largest gland in the body. |
| 3. Large intestine | c. I am 7.5 metre long. |
| 4. Appendix | d. Digestion is impossible without me |
| 5. Lung | e. I play an important role in excretion. |
Answer:
- Lie. My taste buds can tell all tastes – sweet sour, bitter.
- Truth.
- Lie. It is 1.5 metre long.
- Truth.
- Lung → Lie. It plays important role in breathing.
4. Give reasons.
Question 1.
Food becomes acidic in the stomach.
Answer:
- The gastric glands of stomach secrete gastric juice.
- Food that has entered stomach is churned.
- Three components of gastric juice namely hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus are mixed with food here and the food becomes acidic.
Question 2.
Cardiac muscles are said to be involuntary muscles.
Answer:
- Cardiac muscles are found in the heart.
- These muscles bring about the contraction and relaxation (beating) of the heart.
- Their movement is involuntary.
- Cardiac muscles cause our heart to relax and contract continuously at a rate of about 70 times per minute. They do not depend upon our will.
- Beating is carried out in their own fixed manner.
So cardiac muscles are said to be involuntary muscles.
Question 3.
Intoxicating substances should not be consumed.
Answer:
- Physical health is important for our organ system to function properly.
- But harmful habits like smoking, chewing of tobacco, drinking alcohol affect our health adversely.
- If we consume any tobacco products, the mouth, pharynx, alimentary canal, and other organs of the digestive system cannot function properly.
- It causes problems like vomiting, nausea, and headache.
- Tobacco particles stick to teeth, gums, and skin of the mouth cavity and slowly cause injury to those parts resulting in their dysfunction.
- This causes swelling of the gums and pain when moving the jaws.
- The pharynx and intestine become inflamed it progress into cancer leading to death.
Question 4.
Your muscles should be strong and efficient.
Answer:
Muscles are bundles of fibres that can contract and relax as required.
- The action of muscles is necessary for all kinds of movements from the small movements of eyelid to those that demand great strength when chopping wood with an axe.
- We use muscles for various movements like talking laughing, walking, jumping, throwing etc.
- Therefore our muscles should be strong and efficient to do our day today work well and smooth functioning of life processes.
5. Answer the following.
Question a.
How many types of muscles are there? Which are those types?
Answer:
Muscles are bundles of fibres that can contract and relax as required. There are three types of muscles.
- Skeletal muscles.
- Heart or cardiac muscles.
- Smooth muscles.
1. Skeletal muscles: (a) Skeletal muscles work with bones, the two ends of each of these muscles are attached to two different bones. (b) They are responsible for holding the bones of the skeleton together and giving shape to our body, (c) Skeletal muscles permits movement of t the body and maintain the posture of the body. (d) Skeletal muscle is voluntary e.g. muscles in our arms and legs are voluntary muscles, their action depends upon our will. That’s why they are called voluntary muscles.
2. Heart or cardiac muscles: (a) Heart or cardiac muscles bring about the contraction and relaxation (beating) of the heart. (b) Their movement is involuntary, (c) Cardiac muscles cause our heart to relax and contract continuously at a rate of about 70 times per minute, (d) Cardiac muscle is found in heart.
3. Smooth muscles: (a) These muscles are present in the internal organs other than the heart, e.g. muscles of the stomach, intestine, blood vessels, uterus etc. (b)Their movements are involuntary and slow, (c) They are not according to our will. (d) Various vital functions of our body such as digestion, respiration and movement of food material of which we remain quite unaware, are carried out by these special muscles.
Question b.
What causes the problem of acidity? What is its effect on the body?
Answer:
- Stress is the main cause of acidity.
- Hectic lifestyle and stress can lead to unhealthy or irregular meals, not good for digestion process, and this may cause acidity.
- Other reasons are eating spicy food, drinking too much alcohol, missing meals, an empty stomach may lead to acidity.
- Acidity leads to stomach upset, burning sensation in chest and stomach, constriction of blood vessels, weight gain, obesity, cardiovascular damage.
Question c.
Name the different types of teeth. What is the function of each type?
Answer:
There are four types of teeth, namely incisors, canines, pre-molars, and molars.
Each tooth is covered by a hard substance called enamel. Enamel is made up of calcium salt.
The process of digestion begins with the function of the teeth in the mouth.
1. Incisors: (a) These come in first 6-months of age. Incisors are the eight teeth in the front and centre four on top and four on bottom, (b) They are sharp and blade like for cutting food. e.g. for biting an apple, (c) We use them to take first bite of food.
2. Canines: (a) These are strong and pointed, sharpest of all for tearing food. e.g. to tear off a piece of tough meat, (b) They play important role in digestion of food, (c) They appear between 11 and 20 months of age.
3. Pre-molar: Pre molar share features of both canines and molars. (a) You can use them for grinding and chewing food. So that it becomes semi-liquid helping to gulp down the throat easily, (b) They are situated at each side of your mouth in deep settings, (c) They appear at the age of 10 years.
4. Molar: (a) These are broad and flat on top for crushing and grinding food. e.g. to grind up nutmeats. (b) Two teeth above and two teeth below, they appear at the age 11-13 years. (c) Molars are more prone to germ attack because of their remote location in our mouth.
So we should keep them clean.
6. Sketch and label a diagram of the digestive system and describe it in your own words.
Question a.
Sketch and label a diagram of the digestive system and describe it in your own words.
Answer:
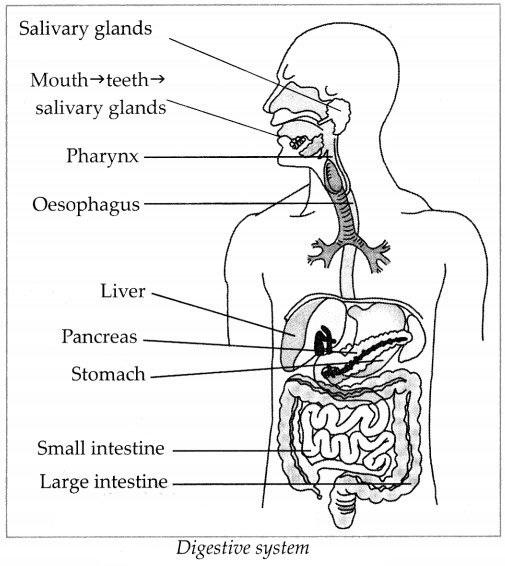
- Conversion of food into a soluble form and its absorption into the blood is called digestion.
- The digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and digestive glands.
- The total length of alimentary canal is about 9 metres.
- Its main parts are the mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus.
- The salivary glands, liver, pancreas are the digestive glands connected to the alimentary canal.
- Different organs of the digestive system perform the function of digestion.
- There are different stages in the process of digestion of food.
- The process of digestion begins with the function of the teeth in the mouth, food is chewed into small pieces.
- There are four types of teeth, incisors, canines, pre-molars and molars.
- Saliva in the mouth contains enzymes, ptyalin, or amylase. It converts starch into maltose.
a. Oesophagus:
- It is a tube leading from the pharynx to the stomach,
- It pushes the food towards the stomach.
b. Stomach:
- The large sac like part of the alimentary canal is called the stomach.
- Food that has entered is churned.
- The gastric glands of stomach secrete gastric juice which contain hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus.
- They mix with food and food becomes acidic.
- Mainly proteins are digested in stomach.
- Due to the churning and actions of gastric juice, food become a semi-solid slurry which is pushed into the small intestine.
c. Small intestine: (6m long)
- Bile secreted by liver mixes with food in small intestine,
- Most of the digestion and absorption of food takes place here.
d. Large intestine: (1.5m long) only water is absorbed in the large intestine. Undigested remain is thrown out of the body through the anus.
Project:
Question 1.
Make charts about maintaining good health.
Question 2.
Design a power point presentation about the digestive system and present it in the class.
Important Questions and Answers
Choose and write the correct word.
Question 1.
The structure that connects bones to the muscles is the ………………….. .
(a) ligament
(b) tendon
(c) fascicle
(d) skin
Answer:
(b) tendon
Question 2.
………………….. is not performed by muscles.
(a) Motion
(b) Excretion
(c) Maintenance of posture
(d) Heat production
Answer:
(d) Heat production
Question 3.
Approximately ………………….. skeletal muscles are there in the human body.
(a) 1000
(b) 600
(c) 100
(d) 60
Answer:
(b) 600
Question 4.
Most of the fat digestion occurs in ………………….. .
(a) rectum
(b) stomach
(c) small intestine
(d) large intestine
Answer:
(c) small intestine
Question 5.
Protein digestion is accomplished in ………………….. .
(a) stomach
(b) ileum
(c) rectum
(d) duodenum
Answer:
(b) ileum
Question 6.
The main function of the muscular system is ………………….. .
(a) excretion
(b) digestion
(c)movement
(d) contraction
Answer:
(c)movement
Question 7.
The largest muscle of our body is in the ………………….. .
(a) arm
(b) face
(c) thigh
(d) None
Answer:
(c) thigh
State whether True or False. Correct the false statement and rewrite:
Question 1.
Saliva is mixed with food in the mouth.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Gastric juice makes food alkaline.
Answer:
False. Gastric juice makes food acidic.
Question 3.
Pancreas is the largest gland in the body.
Answer:
False. Liver is the largest gland in the body.
Question 4.
Food becomes acidic in stomach.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Cardiac muscles are said to be voluntary muscles.
Answer:
False. Cardiac muscles are involuntary.
Question 6.
Muscles contribute 60% of the weight of a healthy adult human body.
Answer:
False. Muscles contribute almost 40% of the weight of a healthy adult human body.
Question 7.
There are about 30 muscles in the human face.
Answer:
True
Question 8.
Muscles in our arms and legs have involuntary muscles.
Answer:
False. Muscles in our arm and legs are voluntary muscles.
Question 9.
Functions of organs like stomach, intestine, heart are carried out by voluntary muscles.
Answer:
False. Functions of these organs are carried out by involuntary muscles.
Question 10.
Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles.
Answer:
True.
Question 11.
The digestive function of the liver is to produce bile.
Answer:
True.
Question 12.
The muscular tissue has the ability to contract or shorten.
Answer:
True.
Find a match for me.
Question 1.
| Column A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Salivary gland | a. Making food acidic |
| 2. Liver | b. Regulation of sugar level |
| 3. Pancreas | c. Digestion of carbohydrates |
| 4. Stomach | d. Digestion of protein, fats, carbohydrate |
Answer:
| Column A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Salivary gland | c. Digestion of carbohydrates |
| 2. Liver | d. Digestion of protein, fats, carbohydrate |
| 3. Pancreas | b. Regulation of sugar level |
| 4. Stomach | a. Making food acidic |
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Saliva | a. Gastric juice |
| 2. Juice in mouth | b. Bile |
| 3. Juice produced by stomach | c. Ptyalin |
| 4. Juice stored by gall bladder | d. Lubricates food |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Saliva | d. Lubricates food |
| 2. Juice in mouth | c. Ptyalin |
| 3. Juice produced by stomach | a. Gastric juice |
| 4. Juice stored by gall bladder | b. Bile |
Question 4.
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Cardiac muscle | a. Inside of organs like stomach |
| 2. Skeletal muscle | b. Found in heart |
| 3. Smooth muscle | c. Attached to bones |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Cardiac muscle | b. Found in heart |
| 2. Skeletal muscle | c. Attached to bones |
| 3. Smooth muscle | a. Inside of organs like stomach |
Find the odd man out:
Question 1.
Stomach, esophagus, liver, small intestine, rectum
Answer:
Liver which is a gland and others are parts of digestive tract.
Question 2.
Saliva, bile, pancreatic juice, gastric juice chyme
Answer:
Chyme, it is a liquid food others are digestive juices.
Name the following:
Question 1.
Gastric juices in stomach
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid, Pepsin, Mucus.
Question 2.
Juices secreted by liver
Answer:
Bile.
Question 3.
Pancreatic juices.
Answer:
Trypsin, Lipase, Amylase.
Question 4.
Salivary gland secretion.
Answer:
Saliva
Question 5.
Enzyme present in saliva.
Answer:
Ptyalin or Amylase.
Question 6.
Types of muscles.
Answer:
Skeletal, Cardiac and Smooth muscles.
Question 7.
Study of muscles.
Answer:
Myology
Give scientific reason:
Question 1.
Skeletal muscles give shape to our body.
Answer:
- Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles. The two ends of each of these muscles are attached to two different bones.
- Muscles of the arms and legs are skeletal muscles.
- They are responsible for holding the bones of the skeleton together and giving shape to our body.
Question 2.
The process of digestion begins in the mouth.
Answer:
- The process of digestion begins with the function of the teeth.
- There are 4 types of teeth – incisors, canines, pre-molar, and molar.
- They are responsible for grinding the food.
- Saliva present in the mouth mixes with the food and makes it soft.
- An enzyme present in saliva called ptyalin amylase converts starch into maltose. Thus, the process of digestion begins in the mouth.
Question 3.
Metabolic processes are impossible without enzymes.
Answer:
- Enzymes are substances secreted’ in the body of an organism which bring about specific chemical reactions.
- Enzymes are specific type of proteins. They are most active at normal body temperature.
- Digestion enzymes of the digestive system bring about changes in the food material.
- Food is digested with the help of enzymes and converted into more soluble and simple form.
Write short notes on:
Question 1.
Voluntary muscles
Answer:
- Working with our hands, walking, eating are functions that depend upon our will.
- Muscles used in these actions are called voluntary muscles, e.g. skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles.
Question 2.
Involuntary muscles
Answer:
- Various processes like breathing, blood circulation, digestion are vital function, essential for life.
- They do not depend upon our will.
- The muscles of organs which carry out these involuntary functions are called involuntary muscles.
- Functions of organs like the stomach, intestine, heart are carried out in their own fixed manner by involuntary muscles, e.g. cardiac muscle present in heart, smooth muscles in lining of stomach, small intestine, blood vessel, uterus.
Question 3.
Muscle and its types
Answer:
There are three types of muscles in body
- Skeletal Muscles
- Cardiac Muscles
- Smooth Muscles
Question 4.
Digestive glands
Answer:
The salivary glands, liver and pancreas are the digestive glands connected to the alimentary canal.
1. Salivary glands: (a) Saliva is produced in the salivary glands in the mouth cavity, located in front of the ears, below the tongue, (b) It is carried to the mouth via ducts, (c) It is mixed with food during the process of chewing.
2. Saliva: contains an enzyme called Ptyalin or salivary amylase. Ptyalin convdrtfe starch into a sugar called maltose.
3. Liver: (a) The liver is the largest gland in the body, (b) Main function is storage of glucose, (c) The digestive juice secreted by the liver is bile, (d) Bile is carried into small intestine, it mixes with food and helps in digestion of fats.
4. Pancreas: The pancreas secretes the pancreatic juice that contains various enzymes
- Trypsin → converts proteins into amino acids.
- Lipase → converts fats into fatty acids, glycerol
- Amylase → converts complex carbohydrate into simple sugar
Question 5.
Enzymes
Answer:
Enzymes are substances secreted in the body an organism which bring about specific chemical reactions.
- Metabolic processes are impossible without enzymes.
- Digestive exzymes of the digestive system bring about changes in the find material.
- They break down the food into simple form.
- They are a type of protein.
- Saliva contain pytalin which converts starch into maltose.
- Trypsin: Convert proteins into amino acids.
- Lipase: Convert fats into fatty acid.
- Amylase: Converts complex carbohydrates into simple sugar.
Question 6.
Draw the structure of the different layers of the tooth.
Answer: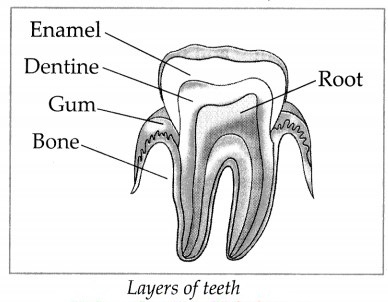
Differentiate between:
Question 1.
Voluntary and Involuntary muscles.
Answer:
| Voluntary muscle | Involuntary muscle |
| 1. Voluntary muscle means you can control it consciously. | 1. Involuntary muscles are controlled by your subconscious. You have no control over them. |
| 2. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles. | 2. Cardiac muscles and smooth muscles are involuntary muscles. |
| 3. Muscles in our arms and legs are voluntary muscles. | 3. Muscles in heart, stomach, blood vessel, intestine are involuntary muscles. |
Question 2.
Skeletal muscle and Cardiac muscle.
Answer:
| Skeletal muscle | Cardiac muscle |
| 1. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles. | 1. Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles. |
| 2. Muscles in our arms and legs are voluntary muscles. | 2. Muscles in heart, stomach, blood vessel, intestine are involuntary muscles. |
| 3. They hold bones of the skeleton together and gives shapes to our body. | 3. They bring about contraction and relaxation of heart. |
Answer the following:
Question 1.
What is meant by organ system?
Answer:
- There are different structural organizational levels in living organism.
- Cells → tissues → organ → organ system → organism
- Different organs together form one organ system.
Question 2.
How are the bones in our body joined to each other?
Answer:
Skeleted muscles join two bones with the help of tendons.
Can you tell?
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What is the mutual relationship between muscles and bones?
Answer:
- Muscles are firmly attached to bones by means of tendons.
- When muscles contract there is movement at the joint and there is pull on tendon which in turn pull on the bones to which they are attached.
Question 2.
Are the muscles of the different organs in our body identical?
Answer:
No, muscles of the different organs are not identical, some are voluntary, some are involuntary.
Question 3.
How do muscles perform their functions?
Answer:
- Muscles in our body always work in groups.
- When some muscles contract other muscles of the same group relax.
- This is how muscles help in proper performance of the various functions of own body.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Which parts of our body are made up only of muscles?
Answer:
Tongue, heart, stomach, liver, pancreas, intestines are made up of only muscles.
Question 2.
What would happen if the cardiac muscles do not move?
Answer:
- Cardiac muscles cause our heart to relax and contract continuously at a rate of about 70 times per minute.
- These muscles bring about the contraction and relaxation (beating) of the heart.
- If the cardiac muscles do not move, heart will stop beating, and will not pump blood to other parts of the body and person will die.
Question 3.
Food enters the stomach and the stomach muscles do not move.
Answer:
- Smooth muscles are present in the lining of stomach.
- Their movement is responsible for churning of food.
- If the muscles do not move, food will not be digested.
Question 4.
During digestion does all the food that we have eaten get converted into useful nutritive substances?
Answer:
- During digestion not all the food is converted into useful nutritive substance, only whatever nutrients we obtain by digestion of food gets absorbed into the blood in small intestine.
- Undigested remains of the food enters the large intestine and thrown out of the body through the anus.
