Chapter 3 Effects of British Rule
Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options:
Question 1.
Portuguese, ………….., French, British participated in the competition of capturing Indian market.
(a) Austrian
(b) Dutch
(c) German
(d) Swedish
Answer:
(b) Dutch
Question 2.
In 1802, Peshwa ………….. signed the Subsidiary Alliance with the British.
(a) Bajirao I
(b) Sawai Madhavrao
(c) Peshwa Nanasaheb
(d) Bajirao II
Answer:
(d) Bajirao II
Question 3.
Jamshedjee Tata started the manufacturing of steel at Tata Iron and Steel Industry established in ………….. .
(a) Mumbai
(b) Kolkata
(c) Jamshedpur
(d) Delhi
Answer:
(c) Jamshedpur
2. Explain the following concept:
Question 1.
Civil Services :
Answer:
- There was a need of bureaucrats to strengthen the British rule in India.
- Lord Cornwallis introduced Civil Services which became an important part of the British government.
- The territories occupied by the British were divided into districts for administrative convenience. The district administration was headed by Collector.
- The officers appointed through the Civil Services (ICS) were taken into administrative services.
Question 2.
Commercialisation of Agriculture :
Answer:
- In the pre-British period, farmers used to cultivate food grains to fulfill domestic need as well as need of the village.
- The British government gave encouragements to the cultivation of cash crops like indigo, cotton, tobacco, tea, etc.
- The shift from cultivation of foodgrains to profit-yielding cash crops is known as Commercialisation of Agriculture.
Question 3.
Economic Policy of British :
Answer:
- Capitalist economy prevailed in England due to the Industrial Revolution.
- This system was brought to India to nurture the British economy.
- It resulted in the economic gains for England but exploitation and impoverishment of India.
3. Explain the following statements with reasons:
Question 1.
Farmers in India became bankrupt.
Answer:
The British made number of changes in the existing system to increase the revenue.
- The payment of revenue was made compulsory in cash and within the prescribed time limit.
- Land was confiscated if the revenue was not paid in time.
- The land revenue collection differed from place to place which resulted in the exploitation of the farmers.
- Farmers were forced to sell their produce to the merchants and middlemen at a low price in order to pay revenue.
- Farmers mortgaged land to pay tax and became indebted to moneylenders.
In this way, the farmers became bankrupt in India.
Question 2.
There was decline of traditional industries in India.
Answer:
- The British government levied heavy duty on the goods exported from India to England.
- The goods imported from England were produced in factories on a large scale and at minimum cost.
- The duty levied on them by British was far too less.
- So, these goods were cheap as compared to traditional goods.
- The Indian artisans found it difficult to compete with low priced British goods.
- Eventually, this led to closing down of traditional industries in India.
4. Complete the following table:
Question.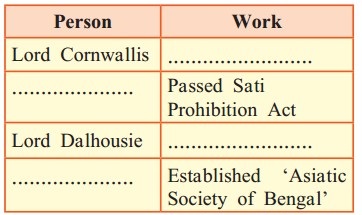
Answer:
Do You Know?
Work done by Chhatrapati Pratapsingh :
- Water tank was built on back side of Yevteshwar temple and Mahadara which supplied water to Satara city.
- He built roads and planted trees on both the sides.
- Sanskrit, Marathi and English was taught to girls and boys in schools.
- Printing press was set up and many books were published.
- A book titled ‘Sabhaniti’ was printed on polity in 1827.
- A road connecting Satara to Mahabaleshwar to Pratapgad was built by him which was further extended to Mahad.aqs
Project:
Prepare detailed information with pictures about the development by British in administration, education, transport and communication in India.
Additional Important Questions and Answers
Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options:
Question 1.
………….. was the main centre of British in western India.
(a) Surat
(b) Cochin
(c) Goa
(d) Mumbai
Answer:
(d) Mumbai
Question 2.
With the treaty of ……………. in 1782 the first Anglo-Maratha war came to an end.
(a) Wadgaon
(b) Vasai
(c) Salbai
(d) Ahmednagar
Answer:
(c) Salbai
Question 3.
In 1848, Lord Dalhousie rejected the adoption policy and annexed the state of ………… .
(a) Pune
(b) Kolhapur
(c) Sangli
(d) Satara
Answer:
(d) Satara
Question 4.
A committee was set up to create a Code of Law, under the leadership of ………… .
(a) Lord Cornwallis
(b) Lord Macaulay
(c) Lord Warren Hastings
(d) Lord Robert Clive
Answer:
(b) Lord Macaulay
Question 5.
……………. started the first textile mill in 1853 at Mumbai.
(a) Jamshedji Tata
(b) Ratan Tata
(c) Kawasjee Nanabhoy Davar
(d) Jamshedji Jeejibhoy
Answer:
(c) Kawasjee Nanabhoy Davar
Question 6.
The first jute mill was set up at in Bengal.
(a) Kolkata
(b) Rishra
(c) Hooghli
(d) Dhakka
Answer:
(b) Rishra
Question 7.
The territory under the control of the English was divided into ………… for the convenience of administration.
(a) Subhas
(b) districts
(c) Paraganas
(d) mahajanpadas
Answer:
(b) districts
Question 8.
The process of giving stress on cultivation of cash crops instead of food grains is known as …………. of agriculture.
(a) Commercialisation
(b) Liberalisation
(c) Globalisation
(d) Rotation
Answer:
(a) Commercialisation
Question 9.
…………… wrote the book ‘Sabhaniti’ in 1827.
(a) Bajirao II
(b) Rango Bapuji Gupte
(c) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj
(d) Chhatrapati Pratapsingh
Answer:
(d) Chhatrapati Pratapsingh
Question 10.
A German thinker …………… was a devout scholar of Indian religion, language and history.
(a) Max Mueller
(b) Lord Macaulay
(c) John Stuart Elphistone
(d) William Jones
Answer:
(a) Max Mueller
Name the following:
Question 1.
He started Subsidiary Alliance.
Answer:
Lord Wellesley
Question 2.
First Governor General according to the Regulating Act.
Answer:
Lord Warren Hastings
Question 3.
He started Dual Government system in Bengal.
Answer:
Robert Clive
Question 4.
Recommended English education in India.
Answer:
Lord Macaulay
Question 5.
Loyal officer of Chhatrapati Pratapsingh.
Answer:
Rango Bapuji Gupte.
Answer the following questions in one sentence each:
Question 1.
How were the officers in administrative services appointed?
Answer:
The officers in the administrative services were appointed through competitive examination known as Indian Civil Services (ICS).
Question 2.
Which principle was introduced by the British in the administration of Justice?
Answer:
The British introduced the principle of ‘equality before law’ in the administration of justice all over British India.
Question 3.
Which factors hindered the growth of new industries in India?
Answer:
The growth of new industries in India was hindered by the lack of British support, capital and experience of management.
Question 4.
Which cash crops were encouraged by the British Government?
Answer:
The British Government gave more encouragement to cash crops like cotton, indigo, tobacco, tea, etc.
Question 5.
Where were the universities established in 1857?
Answer:
The universities were established in Mumbai, Kolkata and Madras (Chennai) in 1857.
Question 6.
What was the effect of development of modern means of transport and communication ?
Answer:
The development of modern means of transport and communication helped to improve communication between the people and strengthened their sense of unity between Indians.
Question 7.
Which values shaped the new era in the 19th century Europe?
Answer:
The new era in the 19th century Europe was shaped on the values humanitarianism, democracy, nationalism and liberalism.
Do as Directed:
1. Complete the concept map:
Question 1.
Answer:
Question 2.
Answer: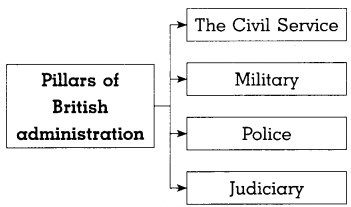
Question 3.
Answer: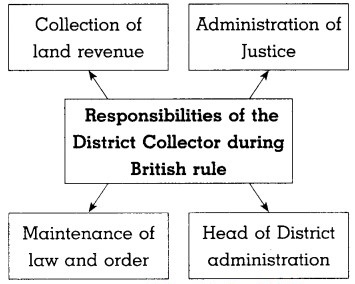
Question 4.
Answer:
2. Complete the following table:
Question 1.
Answer: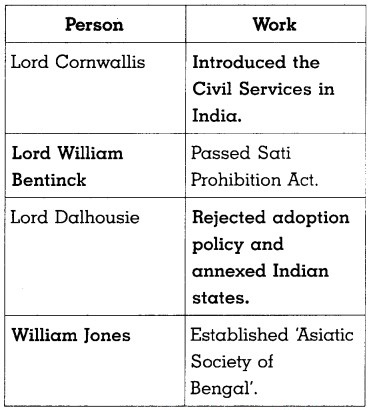
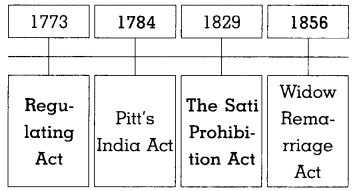
3. Complete the timeline:
Question 1.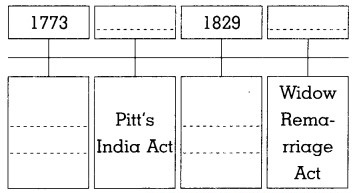
Answer: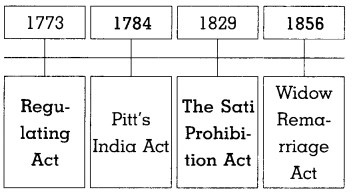
Explain the following concept:
Question 1.
Dual Government :
Answer:
1. The British East India Company in order to consolidate rule introduced new system of governance in India known as Dual Government.
2. It was introduced by Robert Clive in Bengal in 1765 wherein the East India Company took over the revenue collection. The maintenance of law and order was the responsibility of the Nawab of Bengal.
Answer the following in 25-30 words:
Question 1.
What were the conditions laid in Subsidiary Alliance?
Answer:
Lord Wellesley signed Subsidiary Alliance with many Indian rulers in 1798.
Its conditions were :
- Indian rulers should keep the British army in their Court.
- They have to pay the company towards the maintenance of these forces in cash or a part of their territory of equivalent amount of revenue.
- Without the intervention of the British, they would not have any alliance or declare war with any power.
- They should keep the British resident in their court.
Question 2.
What were the provisions in Regulating Act of 1773?
Answer:
According to Regulating Act of 1773:
- The Governor of Bengal was designated as the Governor General. Lord Warren Hastings became the first Governor General of India.
- It gave the Governor General controlling powers over the Bombay and Madras Presidencies.
- It provided a committee of four members to assist the Governor General.
Question 3.
Write about the Pitt’s India Act of 1784.
Answer:
1. The Pitt’s India Act of 1784 established a permanent Board of Control to regulate and manage administration of Company in India.
2. The Board was authorized to issue directives to the Company regarding the governance of India.
Question 4.
Write about the Judicial system introduced by the British in India.
Answer:
- The new Judicial system was introduced in India on the basis of the Judicial system in England.
- Accordingly, each district had a Civil and Criminal Court for the respective cases.
- High Courts were established to reconsider the judgements delivered by the District courts.
Question 5.
What were the functions of the military?
Answer:
- The functions of the military were to defend the Indian territories under the control of the British.
- It was expected to acquire new territories and quell any uprising/revolt against the British India.
Question 6.
What were the defects in the British Judicial System?
Answer:
The defects in the British Judicial System were as follows :
- There were different laws and separate courts for the Europeans.
- It was difficult for the Common people to understand the new laws.
- It was very expensive to fight a legal case.
- The cases got delayed and remained pending for years.
Question 7.
What reforms were introduced in the Judicial System by the British in India?
Answer:
- In the pre-British period, laws were different from place to place.
- There was difference in judgement on the basis of casteism.
- A committee was set up to create a uniform code of law under the leadership of Lord Macaulay.
- The Indian Penal Code was enforced all over British India with British principle of Equality before Law.
Question 8.
Write about introduction of the English education system?
Answer:
- The British were in need of Indians who had received English education in order to run the administration.
- English education was imparted in India according to the recommendations of Lord Macaulay in 1835.
- Indians were introduced to western thoughts, modem reforms, science and technology.
- They realised the need to study their history, culture, religions and also realised the drawbacks.
- The western educated Indian middle class was responsible for initiating social reforms in later period.
Explain the following statements with reasons:
Question 1.
Britishers entered into Maratha politics.
Answer:
1. Marathas had a strong hold on the areas in and around Mumbai which was prime centre of British in western India.
2. British tried to acquire nearby territories but the Marathas checked their expansion.
3. It was only after the death of Peshwa Madhavrao, that they got entry in Maratha politics. Raghunathrao in his greed for Peshwaship sought their help.
This led to the entry of the British in Maratha politics.
Question 2.
The British Parliament introduced some laws to keep control over the affairs of the company.
Answer:
- The ‘Dual Government’ system was introduced by Robert Clive in Bengal in 1765.
- But, sometimes, the officers of the company pocketed money.
- As monopoly of trade was given to East India Company, many trading companies in England envied them.
- The working system of the company was criticised in the British Parliament. So, to keep control on the affairs of the company, the British Parliament introduced some laws.
Question 3.
Salary of company officers were increased.
Answer:
- Lord Cornwallis introduced bureaucracy in India to strengthen the British rule in India.
- He restricted the private trade carried out by the company officers. For this reason, he increased the salary of the company officers.
Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Give an account of the Anglo- Maratha war.
Answer:
- Raghunathrao in his greed for the seat of Peshwa sought help of the British which facilitated their entry into Maratha politics.
- Three wars were fought between Marathas and the British between 1774 to 1818.
- As the Marathas fought unitedly, the Britishers were defeated in the first Anglo- Maratha War in 1782.
- In 1802, Bajirao II entered into Subsidiary Alliance with the British known as the Treaty of Vasai.
- The second Anglo-Maratha War took place as some Maratha Sardars opposed this treaty.
- Marathas were defeated in the second Anglo-Maratha War.
- The defeat of the Marathas led to the increase in interference of the British in the Maratha state.
- Bajirao II declared war against the British as he could not tolerate their interference.
- He lost the war and surrendered to the British in 1818.
Question 2.
Write about the public work done by Chhatrapati Pratapsingh.
Answer:
Chhatrapati Pratapsingh did the following public work :
- Water tank was built by him on the back side of Yevteshwar temple and Mahadara which supplied water to Satara city.
- He built roads and planted trees on both the sides.
- Sanskrit, Marathi and English was taught to girls and boys in schools built by him.
- Printing press was set up and many books were published.
- A book titled ‘Sabhaniti’ was printed on polity in 1827.
- A road connecting Satara – Mahabaleshwar – Pratapgad was built by him. This road was further extended to Mahad.
Question 3.
Compare the Land Revenue Policy in the pre-British period and during the British period.
Answer: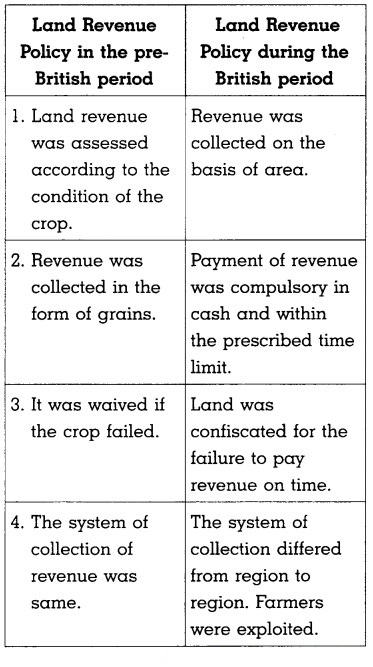
Question 4.
How did the British administrative system benefit India?
Answer:
There were many benefits of British administrative system in India.
- The British introduced railways in India.
- Telegraph system connected major cities and military stations got connected.
- Postal system was also introduced.
- These improved communication generated a sense of unity among the people of India.
- Coal, metal, sugar, cement and chemical industries also developed gradually.
- The western educated Indians learnt the values of humanism, rationalism, democracy, nationalism and liberalism.
- Indians felt the need to study Indian history, religion and traditions.
- Universities were established at Kolkata, Mumbai and Madras (Chennai).
- The newly educated Indian led the social reform movement in later period.
Question 5.
According to you, what were the two positive and two negative effects of British rule on India?
Answer:
The positive effects were :
- English education laid the foundation of future progress in India.
- Indian adopted the principles of freedom, equality and humanity.
The negative effects were :
- The British policy of ‘Divide and Rule’ deepened its roots.
- Regional languages got neglected as English got importance.
