Question 1.
Write the following statements using the symbol of variation.
- Circumference (c) of a circle is directly proportional to its radius (r).
- Consumption of petrol (l) in a car and distance traveled by that car (d) are in direct variation.
Solution:
- c ∝ r
- l ∝ d
Question 2.
Complete the following table considering that the cost of apples and their number are in direct variation.
| Number of apples (x) | 1 | 4 | __ | 12 | __ |
| Cost of apples (y) | 8 | 32 | 56 | __ | 160 |
Solution:
The cost of apples (y) and their number (x) are in direct variation.
∴y ∝ x
∴y = kx …(i)
where k is the constant of variation
i. When, x = 1, y = 8
∴ Substituting, x = 1 and y = 8 in (i), we get y = kx
∴ 8 = k × 1
∴ k = 8
Substituting k = 8 in (i), we get
y = kx
∴ y = 8x …(ii)
This the equation of variation
ii. When,y = 56, x = ?
∴ Substituting y = 56 in (ii), we get
y = 8x
∴ 56 = 8x
∴ x = 56/8
∴ x = 7
iii. When, x = 12, y = ?
∴ Substituting x = 12 in (ii), we get
y = 8x
∴ y = 8 × 12
∴ y = 96
iv. When, y = 160, x = ?
∴ Substituting y = 160 in (ii), we get
y = 8x
∴ 160 = 8x
∴ x = 160/8
∴ x = 20
| Number of apples (x) | 1 | 4 | 7 | 12 | 20 |
| Cost of apples (y) | 8 | 32 | 56 | 96 | 160 |
Question 3.
If m ∝ n and when m = 154, n = 7. Find the value of m, when n = 14.
Solution:
Given that,
m ∝ n
∴ m = kn …(i)
where k is constant of variation.
When m = 154, n = 7
∴ Substituting m = 154 and n = 7 in (i), we get
m = kn
∴ 154 = k × 7
∴ k=154/7
∴ k = 22
Substituting k = 22 in (i), we get
m = kn
∴ m = 22n …(ii)
This is the equation of variation.
When n = 14, m = ?
∴ Substituting n = 14 in (ii), we get
m = 22n
∴ m = 22 × 14
∴ m = 308
Question 4.
If n varies directly as m, complete the following table.
| m | 3 | 5 | 6.5 | __ | 1.25 |
| n | 12 | 20 | __ | 28 | __ |
Solution:
Given, n varies directly as m
∴ n ∝ m
∴ n = km …(i)
where, k is the constant of variation
i. When m = 3, n = 12
∴ Substituting m = 3 and n = 12 in (i), we get
n = km
∴ 12 = k × 3
∴ k=12/3
∴ k = 4
Substituting, k = 4 in (i), we get
n = km
∴ n = 4m …(ii)
This is the equation of variation.
ii. When m = 6.5, n = ?
∴ Substituting, m = 6.5 in (ii), we get
n = 4m
∴ n = 4 × 6.5
∴ n = 26
iii. When n = 28, m = ?
∴ Substituting, n = 28 in (ii), we get
n = 4m
∴ 28 = 4m
∴ 28 = 4m
∴ m=28/4
∴ m = 7
iv. When m = 1.25, n = ?
∴ Substituting m = 1.25 in (ii), we get
n = 4m
∴ n = 4 × 1.25
∴ n = 5
| m | 3 | 5 | 6.5 | 7 | 1.25 |
| n | 12 | 20 | 26 | 28 | 5 |
Question 5.
y varies directly as square root of x. When x = 16, y = 24. Find the constant of variation and equation of variation.
Solution:
Given, y varies directly as square root of x.
∴ y ∝ √4x
∴ y = k √x …(i)
where, k is the constant of variation.
When x = 16 ,y = 24.
∴ Substituting, x = 16 and y = 24 in (i), we get
y = k√x
∴24 = k√16
∴24 = 4k
∴ k=24/4
∴ k = 6
Substituting k = 6 in (i), we get
y = k√x
∴ y = 6√x
This is the equation of variation
∴ The constant of variation is 6 and the equation of variation is y = 6√x .
Question 6.
The total remuneration paid to laborers, employed to harvest soybean is in direct variation with the number of laborers. If remuneration of 4 laborers is Rs 1000, find the remuneration of 17 laborers.
Solution:
Let, m represent total remuneration paid to laborers and n represent number of laborers employed to harvest soybean.
Since, the total remuneration paid to laborers, is in direct variation with the number of laborers.
∴ m ∝ n
∴ m = kn …(i)
where, k = constant of variation
Remuneration of 4 laborers is Rs 1000.
i. e., when n = 4, m = Rs 1000
∴ Substituting, n = 4 and m = 1000 in (i), we get m = kn
∴ 1000 = k × 4
∴ k= 1000/4
∴ k = 250
Substituting, k = 250 in (i), we get
m = kn
∴ m = 250 n …(ii)
This is the equation of variation
Now, we have to find remuneration of 17 laborers.
i. e., when n = 17, m = ?
∴ Substituting n = 17 in (ii), we get
m = 250 n
∴ m = 250 × 17
∴ m = 4250
∴ The remuneration of 17 laborers is Rs 4250.
Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
If the rate of notebooks is Rs 240 per dozen, what is the cost of 3 notebooks?
Also find the cost of 9 notebooks, 24 notebooks and 50 notebooks and complete the following table. (Textbook pg. no. 35)
| Number of notebooks (x) | 12 | 3 | 9 | 24 | 50 | 1 |
| Cost (In Rupees) (y) | 240 | __ | __ | __ | __ | 20 |
Solution:
As the number of notebooks increases their cost also increases.
∴ Number of notebooks and cost of notebooks are in direct proportion.
i.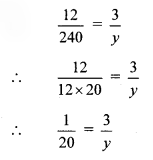
∴ y = 3 × 20
∴ y = 60
ii.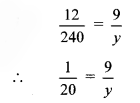
∴ y = 9 × 20
∴ y = 180
iii.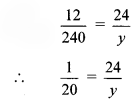
∴ y = 24 × 20
∴ y = 480
iv.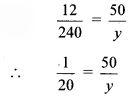
∴ y = 50 × 20
∴ y = 1000
| Number of notebooks (x) | 12 | 3 | 9 | 24 | 50 | 1 |
| Cost (In Rupees) (y) | 240 | 60 | 180 | 480 | 1000 | 20 |
