Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Match the items in column ‘A’ with the proper ones in coloum ‘B’ and explain their impact on the environment.
Column ‘A’ Column ‘B’
1. Harmful waste – a. Glass, rubber, carry bags, etc.
2. Domestic waste – b. Chemicals, pigments, ash, etc.
3. Biomedical waste – c. Radioactive material
4. Industrial waste – d. Left over food, vegetables, peelings of fruits.
5. Urban waste – e. Bandages, cotton, needles, etc.
Answer:
(1 – c),
(2 – d),
(3 – e),
(4 – b),
(5 – a)
2. Complete the statements using the given options and justify those statements. (Geographic favourability, climate, weather, observatory)
a. Of the abiotic factors that affect biodiversity by far the most important is ……………… .
Answer:
Climate.
Climate influences our basic needs like food, clothing and shelter as well as our occupations. Various factors of climate like temperature, atmospheric pressure, sunlight, rainfall, humidity etc. will decide which kind of plants and animals can survive there.
b. A description of the climatic conditions of short duration in a particular area is ……………… .
Answer:
Weather.
Atmospheric conditions at a specific time at a particular place are referred to as weather. Weather is related to a specific location and specific time whereas climate is related to a longer duration and larger area.
c. Irrespective of the progress of human beings, we have to think about ……………… .
Answer:
Geographical favourability.
Geographical favourability includes location, availability of water, availability of natural resources and climate of a region. This has a great impact on the progress of human beings. Countries that have more favourable factors will progress more.
d. Establishments where various climatic factors are recorded are called ……………… .
Answer:
Observatories
Most countries in the world have established meteorology departments for recording climatic factors. These departments have observatories which are equipped with modern instruments and technology.
3. Answer the following questions.
a. How is first aid provided to victims of disasters who are injured?
Answer:
(i) Bleeding: If the victim is injured and bleeding through the wound, the wound should be covered with an antiseptic pad and pressure applied on it for 5 minutes with either thumb or palm.
Fracture and impact on vertebrae: If any bone is fractured, it is essential that the fractured part be immobilized. It can be done with the help of any available wooden rods / batons / rulers. If there is an impact on the back or vertebral column; the patient should be kept immobile on a firm stretcher.
Bums: If victims have bum injuries, it is beneficial to hold the injured part under clean and cold flowing water for at least 10 minutes. How is Solid Waste classified? OR What are the sources of Solid Waste?
Domestic waste: Waste food, paper, plastic paper, plastic bags, vegetable waste, fruit skins, glass and sheet metal articles, etc.
Industrial waste: Chemicals, pigments, sludge, ash, metals, etc.
Hazardous waste: Chemicals generated in various industries, radioactive materials, explosives, infectious materials, etc. Farm/Garden waste: Leaves, flowers, branches of trees, crop residues like straw, animal urine and dung, pesticides, remains of various chemicals and fertilizers, etc.
Electronic waste: Non-functional TV sets, cell phones, music systems, computers and their parts, etc.
Biomedical waste: Bandages, dressings, gloves, needles, saline bottles, medicines, medicine bottles, test tubes, body parts, blood, etc. from clinics, hospitals, blood banks and laboratories. Urban waste: Waste generated through household industries and large commercial and industrial establishments, carry bags, glass, metal pieces and rods, threads, rubber, paper, cans from shops, vegetable and meat markets, construction waste, etc.
(viii) Radioactive waste: Radioactive materials like Strontium-10, Cerium-141, Barium-140 and heavy water, etc. generated from atomic energy plants, uranium mines, atomic research centres, nuclear weapons testing sites, etc.
(ix) Mining waste: Remains of heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cadmium, etc. from mines.
b. State the scientific and eco-friendly methods of waste management.
Answer:
Following are the scientific and eco-friendly methods of waste management:
- Waste separation: In this method, dry and wet wastes are separated, stored and later collected for proper use.
- Composting: Decomposition of degradable kitchen waste in small pits in the backyard, garden or terrace is called composting. Good quality manure can be produced by composting leftover food, peels of fruits, vegetables etc.
- Vermicomposting: Converting solid waste into manure or compost with the help of earthworms is called vermicomposting.
- Vermicompost manure is highly nutritious and can be used for agricultural purposes and garden plants.
- Secured landfill: Solid waste is disposed off in secured landfills.
- The site for secured landfill is selected minimum 2 km away from water bodies and human habitation.
- Care is taken to see that the site does not fall in sensitive zone.
- The landfills are layered with clay and plastic and then the garbage is spread and left to decompose naturally.
- Pyrolysis: In this method, the waste is heated to a high temperature to obtain gas and electricity.
- Semi-combustible waste is burnt in pyrolysis. It is suitable for municipal solid waste management.
- Incineration: Biomedical waste is burnt in incinerators to kill the pathogens. Disinfection and sterilization is also done while treating the biomedical waste.
c. Explain with suitable examples, the relationship between weather forecasting and disaster management.
Answer:
- Depending upon the factors such as storms, clouds, rainfall, etc., weather forecasts are made. It is useful in aviation, shipping, fishing, industries as well as during natural calamities like dust storms, sand storms, heavy rainfall, tsunami etc where proper predictions are made with well equipped satellites and highclass technology.
- Observatories at several locations are doing excellent work in the analysis of the information received from these satellites.
- This data can be used in prevention of losses and danger, improving tolerance, providing relief from disaster, minimising the intensity and extent of harm as well as preparation to face the disaster.
d. Why is e-waste harmful? Express your opinion about this.
Answer:
- e-waste is electronic waste which includes non-functional TV Sets, cell phones, music systems, computers and their parts, etc.
- E-waste contains heavy metals like lead, beryllium, mercury and cadmium.
- These metals accumulate in the soil for long periods and thus affect the biodiversity of the soil.
- Many a times e-waste like battery etc. contain acids which make the soil acidic.
- e-waste can cause ground water pollution, which also affects living organisms when they drink this polluted water.
- Thus, e-waste affects human health and soil microorganisms directly or indirectly.
e. How will you register individual your participation in solid waste management?
Answer:
We can register our individual participation in solid waste management in the following ways:
- Following the 3R mantra: Reduce (reducing the waste), reuse (reuse of waste) and recycle (recycling of waste).
- Throwing plastic wrappers of chocolates, ice-creams, biscuits, etc. into dust bins. Avoid littering.
- Avoiding the use of plastic bags and instead using cloth bags or bags prepared from old sarees, bed-sheets, curtains, etc.
- Using both sides of a paper for writing. Reusing greeting cards and gift papers.
- Avoiding use of tissue paper and preferring to use one’s own handkerchief.
- Using rechargeable batteries instead of lead batteries.
- Implementing various programmes of solid waste management and educating, encouraging the family and society in this regard.
- Avoiding ‘use and throw’ type of articles like pens, canned cold drinks and tetra-packs etc.
4. Write notes.
Meteorology, Climatic factors, Monsoon model, Industrial waste, Plastic waste, Principles of first aid.
5. Give examples of the importance of climate in the living world with explanations, in your own words.
Answer:
- Daily weather as also long term climatic conditions influence human lifestyle directly or indirectly.
- Land, water bodies, plants and animals collectively form the natural environment on earth. This environment is responsible for the development of organisms.
- The climate of a particular region helps to determine the diet, clothing, housing, occupations and lifestyle of the people of that region. For example, the characteristic lifestyle of Kashmiri and Rajasthani people.
- Salinity of marine water, formation of oceanic currents, water cycle, etc. are all related to various weather and climatic factors.
- Various climatic factors bring about the weathering of rocks in the earth’s crust.
- Climate plays a very important role in the formation and enrichment of soil.
- Microbes in the soil play an important role in formation of organic materials. This process depends upon various climatic factors.
6. Explain with suitable examples, the care to be taken when using the methods of transporting patients.
Answer:
- Cradle Method: This method is used for children and under-weight victims.
- Carrying piggy back: This method is used for carrying patients who are unconscious.
- Human crutch method: If one of the legs is injured, the victim should be supported with minimum load on the other leg.
- Pulling or lifting method: This method is used for carrying an unconscious patient, through a short distance.
- Carrying on four-hand chair: This method is used when support is needed for the part below the waist.
- Carrying on two-hand chair: This method is useful for those patients who cannot use their hands but can hold their body upright.
- Stretcher: In an emergency, if a conventional stretcher is not available, then a temporary stretcher can be made using bamboo, blanket, etc.
7. Explain the differences.
a. Weather and climate
Answer:
| Weather | Climate | ||
| (i) | Atmospheric conditions at a specific time at a particular place are referred to as weather. | (i) | The climate of a particular region is the average of daily readings of various weather-related parameters recorded for several years. |
| (ii) | Weather can change continuously. | (ii) | Climate remains constant in a region for a long duration. |
| (iii) | Weather is related to a specific location and specific time. | (iii) | Climate is related to a longer duration and larger area. |
| (iv) | Changes in the weather may occur for short periods of time. | (iv) | Changes in the climate take place slowly over a much long duration. |
b. Degradable and non-degradable waste
Answer:
| Degradable Waste | Non-degradable Waste | ||
| (i) | This type of waste is easily degraded by microbes. | (i) | This type of waste is not easily degraded by microbes because it takes a very long period of time and the use of various techniques. |
| (ii) | It includes kitchen waste (spoiled food, fruits, vegetables), ash, soil, dung, parts of the plants etc. | (ii) | It includes plastic, metal and other similar materials. |
| (iii) | It is also called wet solid waste or wet garbage. | (iii) | It is also called dry solid waste or dry garbage. |
| (iv) | If it is carefully decomposed, we can obtain compost and fuel of good quality from it. | (iv) | It can be recycled. |
Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall?
Environmental Management Class 9 Question 1.
Which natural calamities have you experienced? How did they affect the conditions in your surroundings?
Answer:
In July 2005, heavy rains caused flooding in many parts of Maharashtra including large areas of Mumbai.
They effects were as follows.
- Many people lost life.
- There was water clogging in most parts causing severe damage to private property and public property.
- Hospitals were submerged causing severe inconvenience to patients.
- The city incurred huge financial loss.
Question 2.
How will you make a plan to be safe from calamities or to minimize the damage?
Answer:
- As a responsible citizen we can contribute by educating the people about all the precautions to be taken when such a calamity occurs.
- We can also contribute by minimizing the occurrence of natural calamity like flood by taking measure to reduce land pollution, proper disposing waste material and recycling them.
- We can plan to be safe by keeping the following things handy-torch, first-aid kit, ample food supply and water storage, emergency numbers list and extra pair of clothes.
Thus by taking appropriate measures, we can be safe from calamities
Question 3.
How does the atmosphere affect our daily life?
Answer:
The atmosphere affect our daily life in following ways
- If protects us from harmfull radiations of sun.
- Atmosphere helps to sustain life on earth by providing oxygen for human beings and animal to breathe and carbon dioxide to plants.
- It helps in keeping us warm due to green house effect.
Question 4.
Forecasts about which weather related factors are given during the news bulletins on Doordarshan and Akashvani?
Answer:
Forecasts about different weather related factors such as cloud cover, rain, snowfall, wind speed and temperature are given during the news bulletins on Doordarshan and Akashvani.
Question 5.
What is meant by pollution?
Answer:
Contamination of natural environment that can harmfully affect the ecosystem is called as pollution.
Question 6.
What is meant by solid waste?
Answer:
The waste materials generated through the various daily human activities are called solid waste.
Question 7.
What are the different things included in solid waste?
Answer:
Domestic waste, industrial waste, hazardous waste, electronic waste, biomedical waste, urban waste, radioactive waste and mining waste are the different things included in solid waste.
Question 8.
Why is it necessary to recycle non-degradable waste?
Answer:
(i) non-degradable waste cannot be easily degraded because it takes a very long period of time and the use of various techniques.
(ii) Therefore, non-degradable waste should be recycled so that it does not accumulate and cause hazards to the environment.
Question 9.
Which materials are included in solid dry waste?
Answer:
Solid dry waste includes paper, plastic, metals, glass, cardboard, thermocol etc.
Answer the following
Question 1.
In which different ways do our surroundings get polluted?
Answer:
- Air pollution is caused due to emissions from industries, vehicles, burning of fossil fuels, construction, mining and agriculture.
- Water pollution is caused by domestic sewage and industrial waste water released into the water bodies.
- Soil pollution is caused due to industrial wastes, domestic waste, chemical fertilizers, biomedical waste and pesticides.
- Noise pollution is caused by machines, vehicular traffic, loudspeakers and household appliances.
Question 2.
Which factors are affected favourably or unfavourably by climate? What must we do to minimize the effect?
Answer:
- Climate plays a very important role in our day to day life.
- It influences our basic needs like food, clothing and shelter as well as our occupations.
- Climate is especially important for an agrarian country like India. Also climatic factors like direction and speed of the winds, temperature, atmospheric pressure etc. are also considered during construction work.
- The science of meteorology helps in predicting climatic conditions by satellites in different ways such as prediction of rainfall, air pollution, dust storms, hot and cold waves tsunamic etc.
- so that all the citizens are well-equipped beforehand and can take preventive measures.
Question 3.
Into which two categories can the waste materials in the lists above be classified?
Answer:
The waste materials can be classified as biodegradable waste and non-biodegradable waste.
Answer the following:
Question 1.
Make a list of various waste materials and articles in your area and prepare a chart as follows:
Answer:
Question 1.
Nowadays, an electronic device – the cell phone – is very popular. From a mobile shop near your house, find out how they dispose off old and broken down cell phones.
Answer:
Old and broken down cell phones are sold to scrap dealers, who sell to a bigger dealer where reusable parts are taken out and useless parts are sent for recycling.
Question 2.
What are the different types of casualties that are seen to occur in different types of disasters?
Answer:
- Death.
- Injuries.
- Loss of limbs or body parts.
- Burns.
- Diseases.
- Fractures.
- Bleeding.
- People becoming unconscious.
Question 3.
Which waste management processes are used in your village/town / city?
Answer:
i. The Municipal Corporation or Municipality collects the various kinds of wastes like dry waste, solid waste, biomedical waste in different coloured containers and transports them to areas where they are treated and disposed off.
ii. Industrial waste is mostly recycled and biomedical waste is treated by the scientific methods mentioned below.
a. Solid waste is disposed off in secured land fills. The site for secured landfill is selected 2 km away from water bodies and away from human habitation. Care is taken to see that the site does not fall in sensitive zone. The landfills are layered with clay and plastic and then the garbage is spread and left.
b. Pyrolysis is done for semi combustible material. Semi combustible materials are heated to high temperature by gas arid electricity.
c. The municipality can also set up biogas plants where the solid waste is converted to biogas by anaerobic fermentation. The biogas can be used to generate power and also a good manure which can be used for agriculture.
(d) Biomedical waste is burnt in incinerators to kill the pathogens. Disinfection and sterilization is also done while treating biomedical waste by the Municipal Corporation.
These are some of the waste management processes used in village/town/city.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Observe the garbage collected in the dustbin of your classroom and make a list of the various materials in it.
Discuss with your teacher, how these materials can be properly disposed off. Can we do the same with the garbage generated in our house? Think about it.
Answer:
(i) Garbage collected in classroom dustbin:
- Waste paper and paper bits.
- Pencil shavings
- Wrappers of chocolates, biscuits etc.
- Left over food from tiffins and fruit peels.
- Empty ball pen refills.
(ii) Out of these left over food from tiffins and fruit peels and pencil shaving can be used to make compost manure in school garden. The remaining waste can be sold to scrap dealers and sent for recycling.
(iii) Yes, we can do the same with the garbage generated in the house.
Question 2.
What is the main difference between what we see in the two pictures alongside (A and B).
Answer:
- We see that in picture A there is lot of garbage spread around making the place very dirty, whereas in picture B, there is no garbage and the place is absolutely neat and clean.
Question 3.
What should we do to permanently maintain the condition seen in picture B?
Answer:
To permanently maintain the condition seen in picture B, we should follow the 3R mantra (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle). Also, we must avoid littering, throwing plastic bags, wrappers of chocolates, ice-creams, biscuits etc.
Important Questions and Answers
Choose and write the correct option
Question 1.
is a long term predominant condition of the atmosphere.
(a) Climate
(b) Weather
(c) Pressure
(d) Biosphere
Answer:
(a) Climate
Question 2.
Various climatic factors like are considered during construction of runways, seaports, huge bridges and skyscrapers, etc.
(a) Direction and speed of wind
(b) Temperature
(c) Atmospheric pressure
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 3.
The was established by the United Nations Organization on 23rd March 1950.
(a) World Health Organization
(b) National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration
(c) World Meteorological Organization
(d) Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology
Answer:
(c) World Meteorological Organization
Question 4.
is/are related to various weather and climatic factors.
(a) Salinity of marine water
(b) Formation of ocean currents
(c) Water cycle
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 5.
is the founder of IMD.
(a) Dr. Vasantrao Govarikar
(b) H.F. Blanford
(c) Sir Gilbert Walker
(d) Dr. Radhakrishnan Nair
Answer:
(b) H. F. Blanford
Question 6.
The monsoon model based upon 16 worldwide parameters was developed by the initiative of
(a) Dr. Vasantrao Govarikar
(b) H.F. Blanford
(c) Sir Gilbert Walker
(d) Virghese Kurien
Answer:
(a) Dr. Vasantrao Govarikar
Question 7.
In , forecasts are made taking into account the estimates of current weather related events and ongoing physical activity.
(a) Statistical model
(b) Holistic model
(c) Mathematical model
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Mathematical model
Question 8.
In , predictions are based upon those parameters used in other models which have the greatest effect on the monsoon.
(a) Holistic model
(b) Mathematical model
(c) Statistical model
(d) Scientific model
Answer:
(a) Holistic model
Question 9.
Radioactive materials, explosives and infectious materials are classified as waste.
(a) Industrial waste
(b) Biomedical waste
(c) Urban waste
(d) Hazardous waste
Answer:
(d) Hazardous waste
Question10.
are radioactive waste.
(a) Remains of heavy metals like arsenic, cadmium etc.
(b) Strontium-10, Cerium-141, Barium -140
(c) Waste from blood banks and laboratories
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Strontium-10, Cerium-141, Barium-140
Question 11.
Waste food, paper, plastic, vegetable and fruit waste etc. are classified as waste.
(a) Industrial waste
(b) Farm waste
(c) Domestic waste
(d) Urban waste
Answer:
(c) Domestic waste
Question 12.
is the 3 R mantra.
(a) Refuse, Research, Recycle
(b) Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
(c) Reduce, Reuse, Refuse
(d) Rethink, Recycle, Reuse
Answer:
(b) Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
Question 13.
is the largest producer of electricity from solid waste.
(a) India
(b) America
(c) Japan
(d) China
Answer:
(b) America
Question 14.
Chemicals, pigments, sludge, ash, metals, etc. are classified as waste.
(a) Domestic waste
(b) Industrial waste
(c) Urban waste
(d) Hazardous waste
Answer:
(b) Industrial waste
Question 15.
Period of natural degradation for banana peels is
(a) 1 month
(b) 1-2 weeks
(c) 3-4 weeks
(d) 2 months
Answer:
(c) 3-4 weeks
Question 16.
Period of natural degradation for cloth bags is
(a) 2-3 weeks
(b) 1 month
(c) 5 months
(d) 1 year
Answer:
(b) 1 month
Question 17.
Period of natural degradation for wood is
(a) 1 month
(b) 5 months
(c) 10-15 years
(c) 40-50 years
Answer:
(c) 10-15 years
Question 18.
Period of natural degradation for certain plastic bags is
(a) 50-100 years
(b) infinite duration
(c) 10 lakh years
(d) 1000 years
(c) 10 lakh years
Question 19.
Period of natural degradation for thermocol or Styrofoam cup is
(a) 10 lakh years
(b) infinite duration
(c) 200-250 years
(d) 1 year
Answer:
(b) infinite duration
Question 20.
If any bone is fractured, it is essential that the fractured part be
(a) mobilized
(b) immobilized
(c) pulled
(d) massaged
Answer:
(b) immobilized
Question 21.
For transporting children and under-weight victims, method is used.
(a) carrying piggy back
(b) human crutch method
(c) cradle method
(d) stretcher
Answer:
(c) cradle method
Question 22.
method is useful to carry patients who are unconscious.
(a) Cradle Method
(b) Carrying piggy back
(c) Human crutch
(d) Carrying on four-hand chair
Answer:
(b) Carrying piggy back
Question 23.
method is used for carrying an unconscious patient through a short distance.
(a) Carrying piggy back
(b) Cradle method
(c) Carrying on two-hand chair
(d) Pulling or lifting method
Answer:
(d) Pulling or lifting method
Question 24.
method is useful to carry patients who cannot use their hands but can hold their body upright.
(a) Carrying on four-hand chair
(b) Carrying on two-hand chair
(c) Carrying piggy back
(d) Cradle method
Answer:
(b) Carrying on two-hand chair
Question 25.
method is used to carry patients when support is needed for the part below the waist.
(a) Carrying on four-hand chair
(b) Carrying on two-hand chair
(c) Stretcher
(d) Pulling or lifting method
Answer:
(a) Carrying on four-hand chair
Question 26.
For injuries like sprains, twisting and contusion, should be applied on the injured part.
(a) turmeric powder
(b) antiseptic pad
(c) ice-pack
(d) pressure
Answer:
(c) ice-pack
Find the odd man out:
Question 1.
Waste food, paper, plastic, bandages.
Answer:
Bandages: It is a biomedical waste whereas the others are domestic waste.
Question 2.
Pesticides, fertilizers, crop residue, sludge.
Answer:
Sludge: It is an industrial waste whereas the others are farm waste.
Question 3.
Strontium -10, Cerium – 141, Barium – 140, Cadmium.
Answer:
Cadmium: It is a mining waste whereas the others are radioactive waste.
Question 4.
Banana peels, cloth bag, food waste, plastic bag.
Answer:
Plastic bag: It is a non-biodegradable waste whereas the others are degradable wastes.
Question 5.
Fruits, ash, metals, vegetables.
Answer:
Metal: It is a non-biodegradable waste whereas the others are degradable wastes.
Complete the analogy:
(1) Specific duration and specific time: Weather : : Longer duration and longer time :
(2) Mumbai: 5000 tons solid waste :: Pune:
(3) Kitchen waste, parts of plants : Wet solid waste :: Plastic, metals :
(4) Largest producer of electricity from solid waste : America : : Production of useful materials from banana peelings :
(5) Cloth bags : 1 month : : Rags :
(6) Tin cans : 50-100 years : : Aluminium cans :
(7) Wood : 10-15 years :: Styrofoam :
Answer:
(1) Climate
(2) 1700 tons solid waste
(3) Dry solid waste
(4) Japan
(5) 5 months
(6) 200-250 years
(7) Infinite duration
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Mining waste | (a) Leaves, flowers, crop residue. |
| (2) Electronic waste | (b) Remains of heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cadmium. |
| (3) Farm waste | (c) Strontium-10, Cerium-141, Barium-140 |
| (4) Radioactive waste | (d) Cell phones, TV sets, Computers |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – d),
(3 – a),
(4 – c)
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Banana peels | (a) 10 lakh years. |
| (2) Plastic bags | (b) 200-250 years. |
| (3) Leather shoes | (c) 3-4 weeks |
| (4) Aluminium cans | (d) 40-50 years |
Answer:
(1 – c),
(2 – a),
(3 – d),
(4 -b)
Question 3.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Thermocol (2) Tin cans (3) Woollen socks (4) Wood | (a) 1 year. (b) Infinite duration. (c) 10-15 years (d) 50-100 years |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – d),
(3 – a),
(4 – c)
State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statements:
Question 1.
Climate is a long term predominant condition of the atmosphere.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Climate changes continuously.
Answer:
False. Climate does not change continuously. It remains constant in a region for a long duration.
Question 3.
If present climatic conditions are analysed with reference to the past climatic conditions, we can predict climatic changes of the future.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Forecasting is difficult for places where climatic changes are slow and of a limited nature.
Answer:
False. Forecasting is easy for places where climatic changes are slow and of a limited nature.
Question 5.
Climate plays a very important role in the formation and enrichment of soil.
Answer:
True.
Question 6.
Prediction maps are prepared once in 24 hours.
Answer:
False. Prediction maps are prepared twice in every 24 hours.
Question 7.
The first prediction of monsoon in India was made by Dr. Vasantrao Govariakar.
Answer:
False. The first prediction of monsoon in India was made my H.F. Blanford.
Question 8.
H.F. Blanford used the rainfall in Kerala as the parameter for prediction of monsoon in India.
Answer:
False. H.F. Blanford used the snowfall in Himalayas as a parameter for prediction of monsoon in India.
Question 9.
In Holistic model, predictions are made taking into account estimates of current weather-related events and ongoing physical interactions between them.
Answer:
False. In Holistic model, predictions are based upon those parameters used in other models which have the greatest effect on monsoon.
Question 10.
Any meteorological model depends upon the inter-relationships between parameters used in that model and the results expected from it.
Answer:
True.
Question 11.
Remains of heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cadmium, etc. from mines are industrial waste.
Answer:
False. Remains of heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cadmium etc. from mines are mining waste.
Question 12.
Use of ‘use and throw’ type of articles like pens, canned cold drinks, tetra packs should be encouraged in waste management.
Answer:
False. Use of ‘use and throw’ type of articles like pens, canned cold drinks, tetra packs should be strictly avoided in waste management.
Question 13.
We should use tissue paper instead of one’s own handkerchief for effective waste management.
Answer:
False. We should use one’s own handkerchief instead of tissue paper for effective waste management.
Question 14.
Certain plastic bags take 1 month to degrade.
Answer:
False. Certain plastic bags take 10 lakh years to degrade.
Question 15.
Banana peels can degrade in 3-4 weeks.
Answer:
True.
Question 16.
If the victim has burn injuries, it is beneficial to cover the burnt part with blanket.
Answer:
False. If the victim has burn injuries, it is beneficial to hold the injured part under clean and cold flowing water for at least 10 minutes.
Question 17.
CPR helps to bring the circulation to normal.
Answer:
True.
Question 18.
If breathing has stopped, the head should be held in backward sloping position.
Answer:
False. If breathing has stopped, the victim should be given artificial ventilation by mouth to mouth resuscitation.
Question 19.
Japan is the largest producer of electricity from solid waste.
Answer:
False. America is the largest producer of electricity from solid waste.
Question 20.
China has developed the projects of production of threads, paper and other useful materials from banana peels.
Answer:
False. Japan has developed the projects of production of threads, paper and other useful materials from banana peels.
Define the following:
Question 1.
Weather
Answer:
Atmospheric conditions at a specific time at a particular place are referred to as weather.
Question 2.
Climate
Answer:
The climate of a particular region is the average of daily readings of various weather-related parameters recorded for several years.
Question 3.
Meteorology
Answer:
The science that studies the inter-relationships between the various components of air, natural cycles, geological movements of earth and climate is called meteorology.
Question 4.
Solid waste
Answer:
Waste materials generated through daily human activities are called solid waste.
Question 5.
Urban waste
Answer:
Waste generated through household industries and large commercial and industrial establishments is called Urban waste.
Answer the following:
Question 1.
What is the necessity of solid waste management?
Answer:
Necessity of solid waste management:
- For preventing environmental pollution and to keep the surroundings clean.
- For energy as well as fertilizer production and through that to generate work and employment opportunities.
- To reduce the strain on natural resources through treatment of solid waste.
- To improve the health and quality of life and to maintain environmental balance.
Question 2.
What are the harmful effects of solid waste?
Answer:
Harmful effects of solid waste:
- Effect on biodiversity.
- Releases bad odour.
- Produces toxic gases.
- Leads to degradation of natural beauty.
- Leads to pollution of air, water and soil.
- Spreads diseases.
Question 3.
What first-aid should be given for injuries like sprains, twisting and contusion?
Answer:
For injuries like sprains, twisting and contusion, the ‘RICE’ remedy should be applied:
- Rest: Allow the victim to sit in a relaxed position.
- Ice: Apply an ice-pack to the injured part.
- Compression: After the ice-pack treatment, the injured part should be massaged gently.
- Elevate: The injured part should be kept in a raised/elevated position.
Question 4.
Why do meteorological models need to be changed continually?
Answer:
- Any meteorological model depends upon the inter-relationship between parameters used in that model and the results expected from it.
- However, as these inter-relationships with reference to the ocean and atmosphere are never constant, meteorological models need to be changed continually.
Question 5.
What is urban waste? What does it include?
Answer:
- Waste generated through household industries and large commercial and industrial establishments is called urban waste.
- It includes carry bags, glass, metal pieces and rods, threads, rubber, paper, cans from shops, waste from vegetable and meat markets, construction waste etc.
Question 6.
What does biomedical waste include?
Answer:
biomedical waste includes bandages, dressings, gloves, needles, saline bottle, medicines, medicine bottles, test tubes, body parts, blood etc. from clinics, hospitals, blood banks and laboratories.
Write short notes on:
Question 1.
Meteorology
Answer:
- The science that studies the inter-relationship between the various components of air, natural cycles, geological movements of the earth and climate is called meteorology.
- Meteorology includes the study of storms, clouds, rainfall, thunder, lightning etc.
- Depending upon the study of such factors, weather forecasts are made.
- They are useful to common people, farmers, fisheries, aviation services, water transport and various other organizations.
Question 2.
Climatic factors
Answer:
- The climate of a particular region is the average of daily readings of various weather-related parameters recorded for several years.
- Climatic factors include direction and speed of wind, temperature, atmospheric pressure, clouds, rainfall, humidity, visibility etc.
- These factors influence our basic needs like food, clothing, shelter as well as our occupations.
- Various climatic factors bring about the weathering of rocks in the earth’s crust.
- Microbes in the soil play an important role in formation of organic materials. This process also depends upon various climatic factors.
Question 3.
Monsoon model
Answer:
- The tradition of forecasting the monsoon season in India is older than 100 years.
- After the famine of 1877, H.F. Blanford, the founder of IMD had made such a prediction for the first time taking the snowfall in the Himalayas as a parameter for this prediction.
- In the decade of the 1930’s, the then director of IMD, Sir Gilbert Walker had underlined the relationship between various worldwide climatic factors and the Indian monsoon and based on available observations and previous recordings related to this relationship, he put forth a hypothesis regarding the nature of the monsoon.
- With the initiative of Dr. Vasantrao Govarikar in the decade of the 1990’s, a monsoon model based upon 16 worldwide climatic parameters was developed. This model was in use from 1990 to 2002.
- Presently, new models are being developed at IITM. Work is in progress at two levels, namely designing new models and developing new technology.
- The main focus is on the development of the radar system and satellite technology.
Question 4.
Plastic waste
Answer:
- Plastic waste is the accumulation of plastic products in the environment that adversely affects environment, humans and animals.
- Plastic waste is excessively generated as plastic is inexpensive and durable.
- Plastic is slow to degrade. It takes around 10 lakh years for certain plastic bags to degrade. .
- Plastic waste affects land and water.
- It also affects the health of animals, cattle unknowingly ingest these plastic bags leading to stomach cancer in them.
- Plastic also releases toxic chemicals which are carcinogenic to humAnswer:
- To avoid plastic waste, cloth bags should be used instead of plastic bags. Plastic articles should be recycled.
Question 5.
Industrial waste
Answer:
- Industrial waste is the waste produced by industrial processes or activities.
- There is a huge variety of industries producing different types of materials and articles. All of these use raw materials and give out a lot of waste.
- There are hundreds of mines which extract copper, silver, gold, iron, coal etc. Huge quantities of waste are produced while processing them.
- Cement industries give out solid, liquid and gaseous wastes.
- While refining crude oil, a lot of poisonous gaseous and liquid wastes are produced.
- Construction units produce huge quantities of waste stones, pebbles, broken bricks, wood waste etc. Mostly they are dumped in landfills.
- It also includes chemicals, pigments, sludge, ash, metal, etc. given out from mining, textile, construction, chemical industries.
Question 6.
Principles of first aid
Answer:
Life and Resuscitation – ‘ABC’ is the Basic Principle of first aid which is provided to the victims of disaster.
- Airway: If the victim has difficulty in breathing, the head should be held in a backward sloping position or the chin should be raised so that the respiratory passage remains open.
- Breathing: If breathing has stopped, the victim should be given artificial ventilation by mouth to mouth resuscitation.
- Circulation: If the victim is unconscious, then after giving mouth to mouth respiration twice,
Question 7.
Statistical Model
Answer:
- In this model, current climatic observations in a region are compared with earlier parameters such as oceanic temperature, atmospheric” pressure and the nature of the monsoon rainfall for several years.
- This data is comparatively analysed by statistical methods and predictions are made about the monsoon in the present conditions.
Question 9.
Holistic Model
Answer:
- In this model, predictions are based upon those parameters used in other models which have the greatest effect on the monsoon.
- Nowadays, predictions declared by IMD are the collective outcome of various model. This is called a holistic model.
Complete the following concept chart:
Question 1.
Weather-related climatic factors
Answer: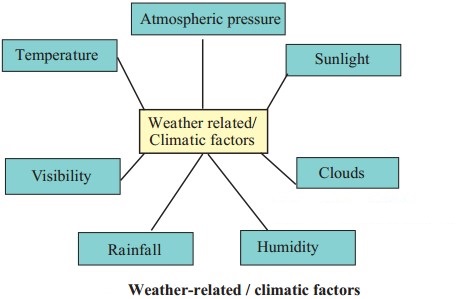
Question 2.
Harmful effects of solid waste
Answer:
Question 3.
Scientific and eco-friendly waste Management
Answer: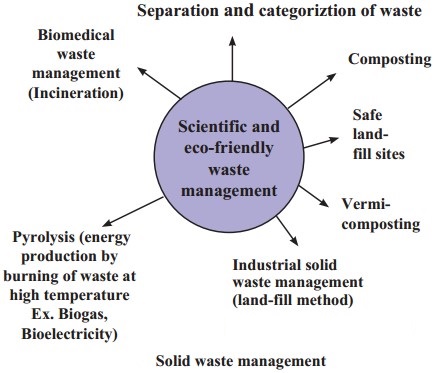
Answer in detail:
Question 1.
What are the principles of solid waste management?
Answer:
Principles of solid waste management:
- Reuse: After use, materials should be reused for some other proper purposes.
- Refuse: Refusal to use articles made from non- degradable articles like plastic and thermocol.
- Recycle: Production of useful articles by recycling solid wastes. For example, paper and glass can be recycled.
- Rethink: Rethinking our habits, activities and their consequences in connection with the use of various articles of daily use.
- Reduce: Restricting the use of resources to avoid their wastage.
- Old materials should be reused. One thing should be shared by many, use and throw type of objects should be avoided.
- Research: Conducting research related to reuse of materials that are temporarily out of use.
- Regulation and Public awareness: Following the laws and rules related to waste management and motivating others to do the same.
Question 2.
What is disaster management? What actions does it include?
Answer:
Disaster management is action implemented through proper planning, organized activity and co-ordination.
It includes the following:
- Prevention of loss and danger.
- Improving tolerance.
- Providing relief from disaster, minimising the intensity and extent of harm.
- Preparation to face the disaster.
- Immediate action in the disaster situation.
- Assessment of damages and intensity of the disaster.
- Arranging for rescue work and help.
- Rehabilitation and rebuilding.
Question 3.
Write a short note on : Indian Meteorological Department
Answer:
- The Indian Meteorological Department was founded by the British in 1875 at Shimla.
- Its head office is at Pune and its Regional offices are at Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Nagpur and Delhi.
- Maps are prepared every day which indicate the daily predictions about the weather.
- Such maps are prepared and published twice in every 24 hours.
- In this institute, research goes on continuously on various aspects like instruments for climatic readings, predictions made about climate using radar, predictions about climate related to seismology, predictions regarding rainfall by satellites, air pollution etc.
- The Indian Meteorological Department provides information regarding weather and climatic conditions to other departments like aviation, shipping, agriculture, irrigation, marine oil exploration and production etc.
- Predictions regarding calamities like dust storms, sand storms, heavy rainfall, hot and cold waves, tsunami, etc. are communicated to various departments, all types of mass communication media and all citizens.
- India has launched several satellites equipped with highclass technology.
- Observatories at several locations are doing excellent work in the analysis of the information received from these satellites.
